| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
磷酸氢锶
CAS:13450-99-2 |
|
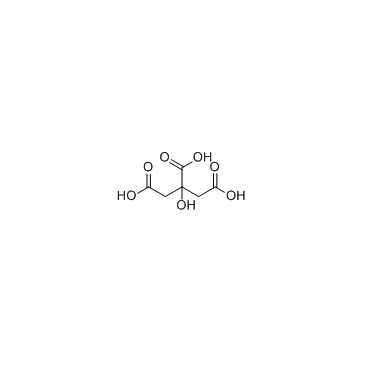 |
柠檬酸
CAS:77-92-9 |
|
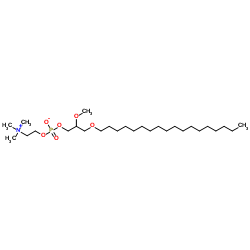 |
依地芬
CAS:70641-51-9 |
|
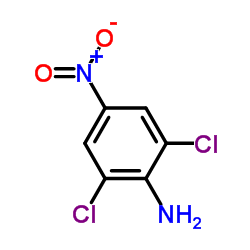 |
2,6-二氯-4-硝基苯胺
CAS:99-30-9 |
|
 |
丁卡因碱
CAS:5094-24-6 |