| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
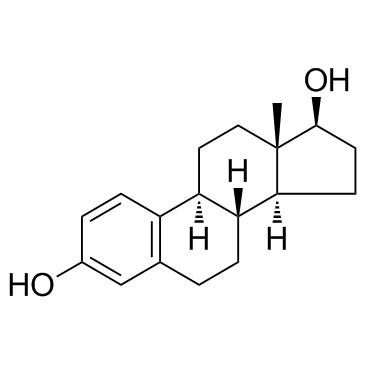 |
雌二醇
CAS:50-28-2 |
|
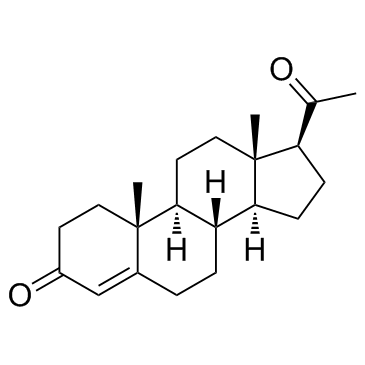 |
孕酮; 黄体素; 黄体酮
CAS:57-83-0 |
|
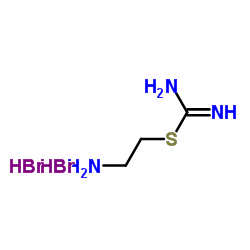 |
S-(2-氨乙基)异硫脲溴鎓氢溴酸盐
CAS:56-10-0 |
|
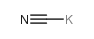 |
氰化钾
CAS:151-50-8 |