Antinociceptive effects of galanin in the central nucleus of amygdala of rats, an involvement of opioid receptors.
Wu-Yang Jin, Zhuo Liu, Dong Liu, Long-Chuan Yu
文献索引:Brain Res. 1320 , 16-21, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The central nucleus of amygdala (CeA) is a very important brain structure involved in multiple physiological functions, especially in pain modulation. There are high densities of galanin and galanin receptors found in the CeA. The present study was performed to explore the antinociceptive effects of galanin in the CeA of rats, and possible involvements of opioid receptors in the galanin-induced antinociception. Intra-CeA injection of galanin induced dose-dependent increases in hindpaw withdrawal latencies (HWLs) to noxious thermal and mechanical stimulations in rats. Interestingly, the amtinociceptive effect induced by intra-CeA injection of galanin was blocked by intra-CeA injection of naloxone, a common opioid receptor antagonist, indicating an involvement of opioid receptors in the galanin-induced antinociception in the CeA of rats. Moreover, intra-CeA injection of either selective mu-opioid receptor antagonist beta-funaltrexamine (beta-FNA) or delta-opioid receptor antagonist naltrindole, but not kappa-opioid receptor antagonist nor-binaltorphimine (nor-BNI), significantly attenuated the galanin-induced increases in HWLs in the CeA of rats. Taken together, the results demonstrate that galanin induces antinociceptive effects in the CeA of rats, and both mu- and delta-opioid receptors are involved in the galanin-induced antinociception.Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
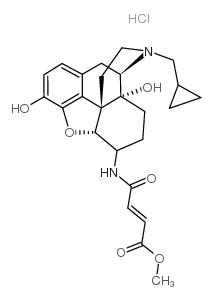 |
β-富纳曲胺盐酸盐
CAS:72786-10-8 |
C25H31ClN2O6 |
|
Novel orally available salvinorin A analog PR-38 inhibits ga...
2014-07-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 350(1) , 69-78, (2014)] |
|
Activation of the cloned human kappa opioid receptor by agon...
1997-08-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 282 , 676, (1997)] |
|
Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-mammalian ta...
2010-11-24 [Neuroscience 171(1) , 134-43, (2010)] |
|
The mu-opioid receptor-selective peptide antagonists, antana...
2013-01-10 [Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 40 , 126-31, (2013)] |
|
The involvement of micro-opioid receptors in the central ner...
2010-01-01 [Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 152(4) , 342-52, (2010)] |