| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
乙醇
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
维生素A酸; 视黄酸
CAS:302-79-4 |
|
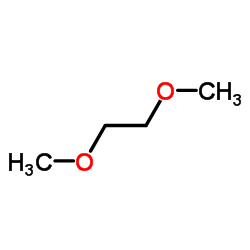 |
乙二醇二甲醚
CAS:110-71-4 |
|
 |
氢化可的松
CAS:50-23-7 |
|
![4-(4-甲基哌嗪-1-基)-7-(三氟甲基)吡咯并[1,2-a]喹喔啉马来酸盐 结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/369/1350965-83-1.png) |
4-(4-甲基哌嗪-1-基)-7-(三氟甲基)吡咯并[1,2-a]喹喔啉马来酸盐
CAS:1350965-83-1 |