| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
海藻酸钠
CAS:9005-38-3 |
|
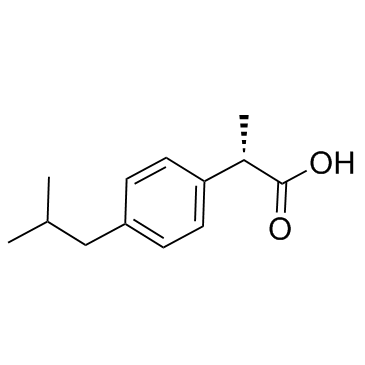 |
(S)-(+)-布洛芬
CAS:51146-56-6 |
|
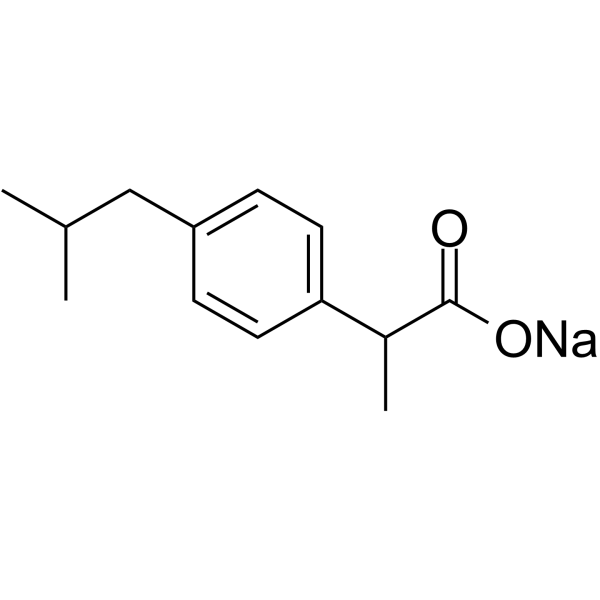 |
布洛芬钠盐
CAS:31121-93-4 |
|
 |
布洛芬
CAS:15687-27-1 |
|
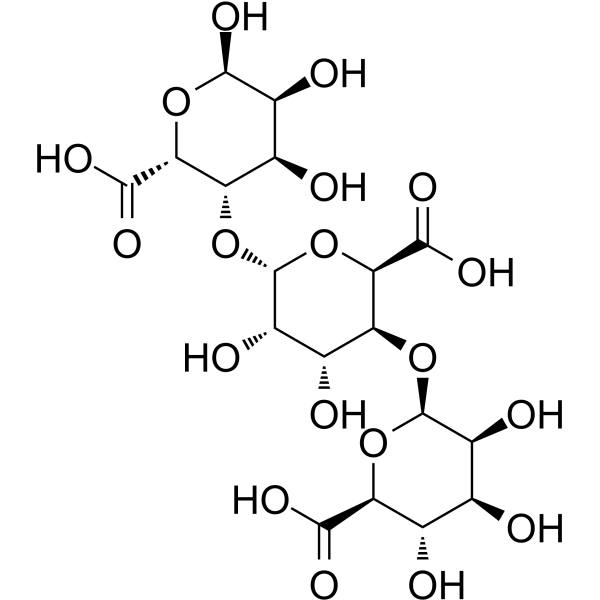 |
海藻酸
CAS:9005-32-7 |
|
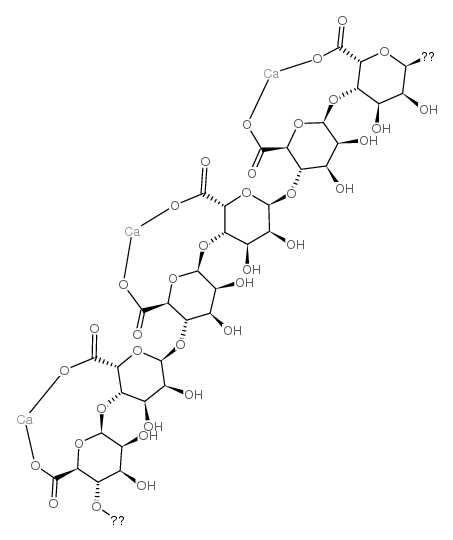 |
海藻酸钙
CAS:9005-35-0 |