| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氯化钠
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
咖啡因
CAS:58-08-2 |
|
 |
无水氯化钙
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
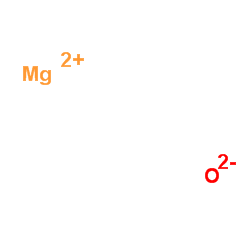 |
氧化镁
CAS:1309-48-4 |
|
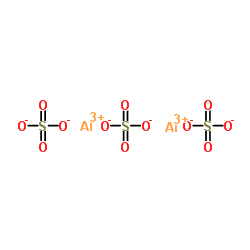 |
硫酸铝
CAS:10043-01-3 |
|
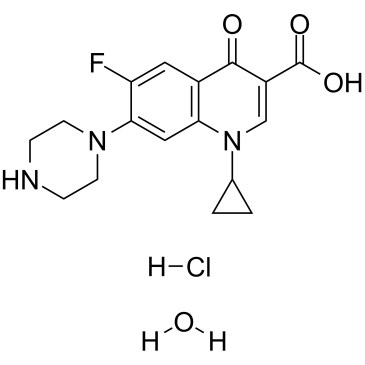 |
盐酸环丙沙星
CAS:86393-32-0 |
|
 |
氯化钠-35cl
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
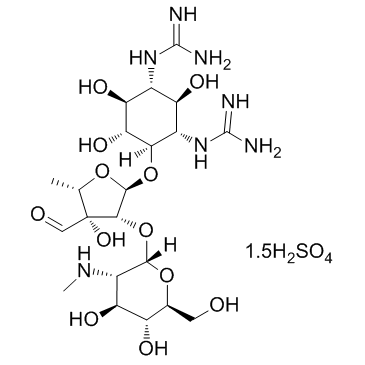 |
硫酸链霉素
CAS:3810-74-0 |
|
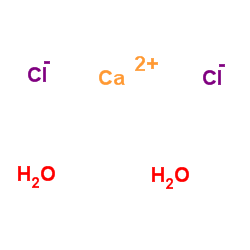 |
二水氯化钙
CAS:10035-04-8 |