| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
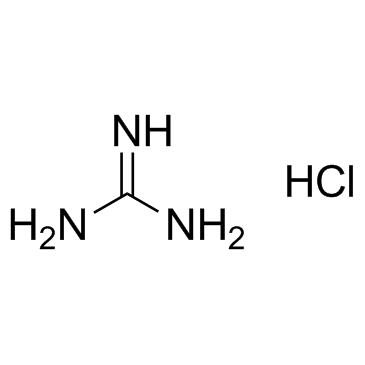 |
盐酸胍
CAS:50-01-1 |
|
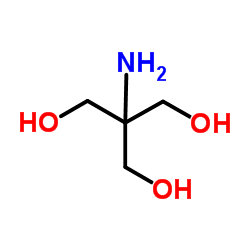 |
三(羟甲基)氨基甲烷
CAS:77-86-1 |
|
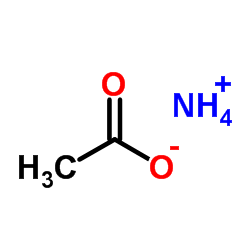 |
乙酸铵
CAS:631-61-8 |
|
 |
4-(2-氨乙基)苯磺酰氟盐酸盐(AEBSF)
CAS:30827-99-7 |
|
 |
二甲基亚砜
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
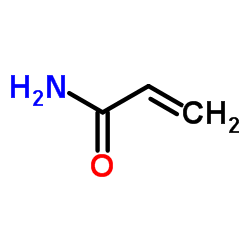 |
丙烯酰胺
CAS:79-06-1 |
|
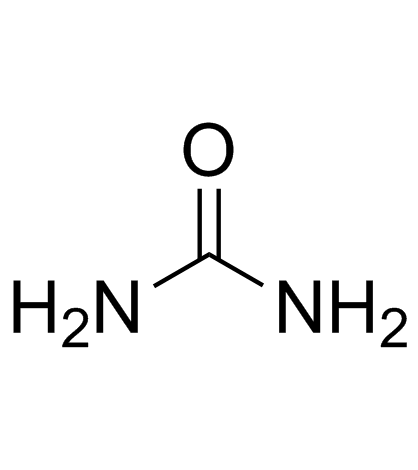 |
尿素
CAS:57-13-6 |
|
 |
2-氨基吖啶酮
CAS:27918-14-5 |
|
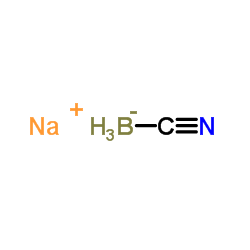 |
氰基硼氢钠
CAS:25895-60-7 |
|
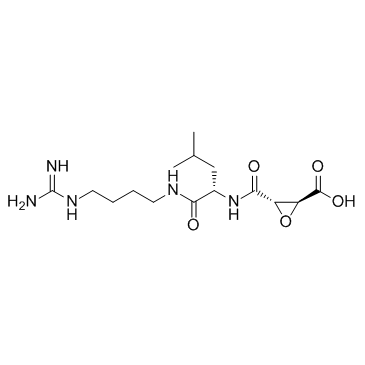 |
N-(反式-环氧丁二酰基)-L-亮氨酸-4-胍基丁基酰胺
CAS:66701-25-5 |