| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
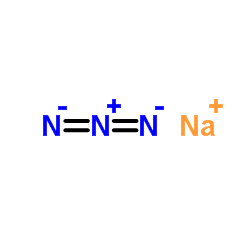 |
叠氮化钠
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
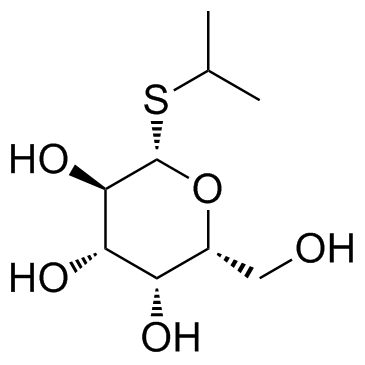 |
异丙基-β-D-硫代半乳糖苷(IPTG)
CAS:367-93-1 |
|
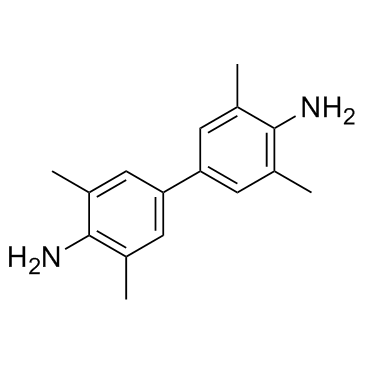 |
3,3′,5,5′-四甲基联苯胺(TMB)
CAS:54827-17-7 |
|
 |
L-赖氨酸盐酸盐
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
 |
链霉蛋白酶E
CAS:9036-06-0 |