| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
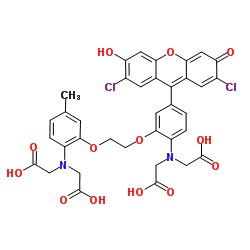 |
荧光钙探针FLUO-3
CAS:123632-39-3 |
|
 |
氯化锌
CAS:7646-85-7 |
|
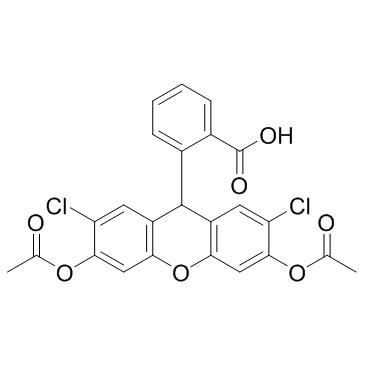 |
2-(3,6-二乙酰氧基-2,7-二氯-9H-氧杂蒽-9-基)苯甲酸
CAS:4091-99-0 |
|
 |
碘化丙啶
CAS:25535-16-4 |