| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
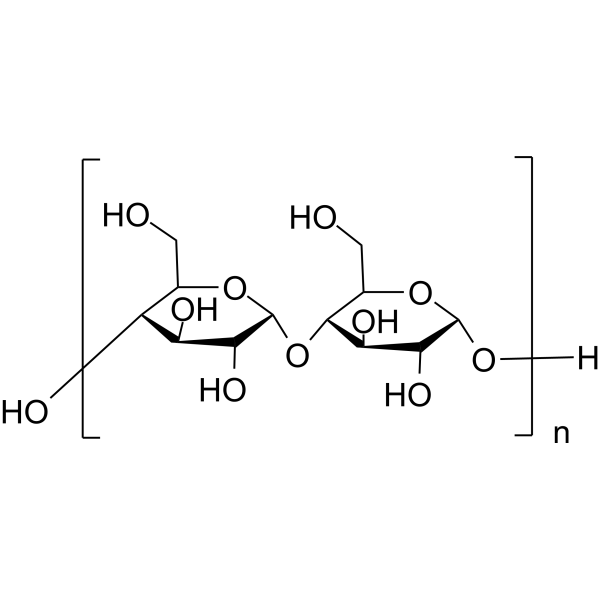 |
马铃薯淀粉
CAS:9005-25-8 |
|
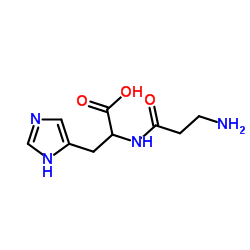 |
α-淀粉酶(高温淀粉酶)
CAS:9001-19-8 |
|
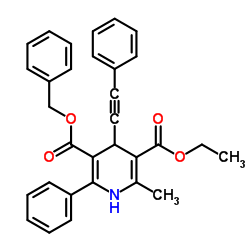 |
α-淀粉酶,来源于解淀粉芽胞杆菌
CAS:9000-85-5 |
|
 |
α-淀粉酶
CAS:9000-90-2 |
|
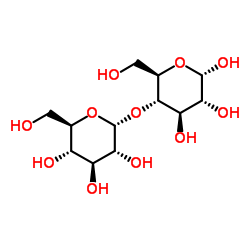 |
可溶性淀粉
CAS:9005-84-9 |