| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
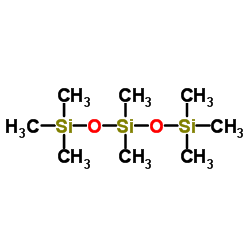 |
八甲基三硅氧烷
CAS:107-51-7 |
|
 |
乙醇
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
六甲基二硅氧烷
CAS:107-46-0 |
|
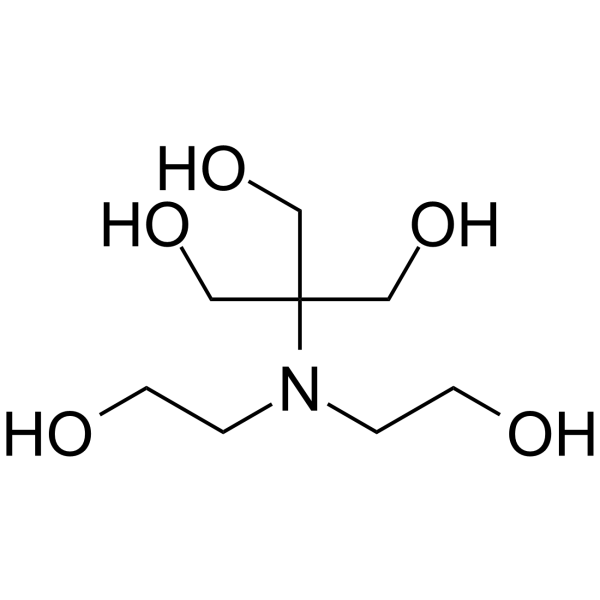 |
二(2-羟乙基)亚氨基三(羟甲基)甲烷
CAS:6976-37-0 |
|
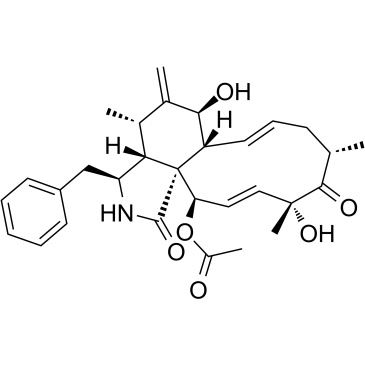 |
细胞松弛素D
CAS:22144-77-0 |
|
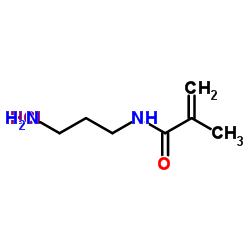 |
N-(3- 氨丙基)甲基丙烯酰胺 盐酸盐
CAS:72607-53-5 |