| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
环孢霉素A
CAS:59865-13-3 |
|
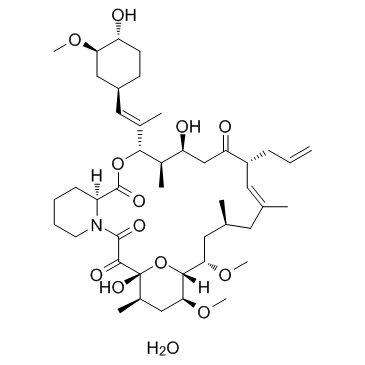 |
他克莫司
CAS:109581-93-3 |
|
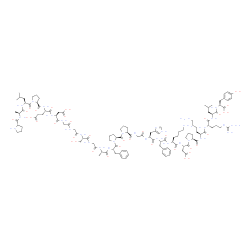 |
重组人碱性成纤维细胞生长因子OsrhbFGF
CAS:62031-54-3 |