| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
β-烟酰胺单核苷酸
CAS:1094-61-7 |
|
 |
甘氨酸
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
 |
十二烷基硫酸钠
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
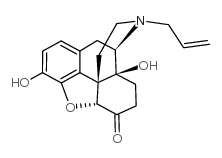 |
纳洛酮
CAS:465-65-6 |
|
 |
DL-丝氨酸
CAS:302-84-1 |
|
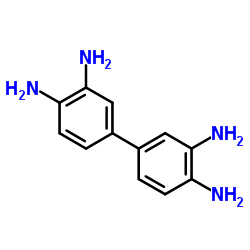 |
3,3'-二氨基联苯胺
CAS:91-95-2 |
|
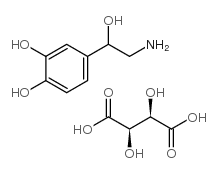 |
(±)-去甲肾上腺素酒石酸氢盐
CAS:3414-63-9 |
|
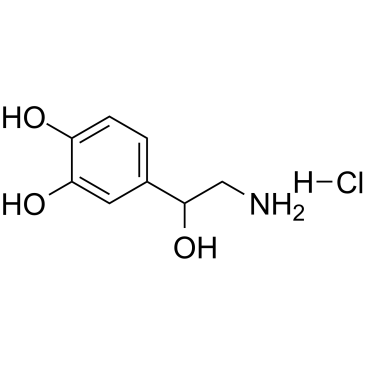 |
DL-去甲肾上腺素 盐酸盐
CAS:55-27-6 |
|
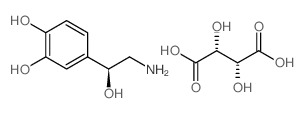 |
D-去甲肾上腺素 酒石酸氢盐
CAS:636-88-4 |
|
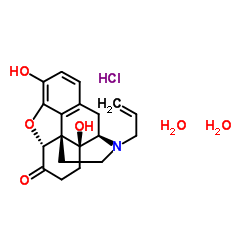 |
二水合盐酸纳洛酮
CAS:51481-60-8 |