| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
柚皮苷
CAS:10236-47-2 |
|
 |
甲酸
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
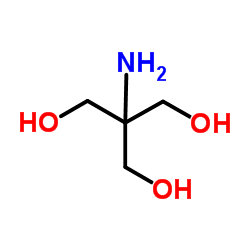 |
三(羟甲基)氨基甲烷
CAS:77-86-1 |
|
 |
乙醇
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
甲醇
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
氯化镁
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
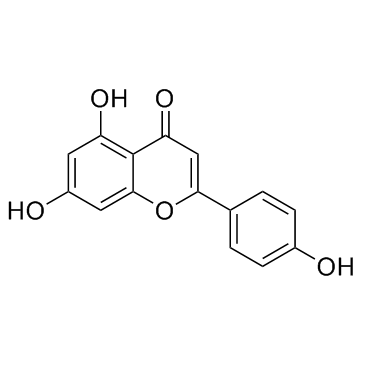 |
芹菜素; 芹黄素; 5,7,4'-三羟基黄酮
CAS:520-36-5 |
|
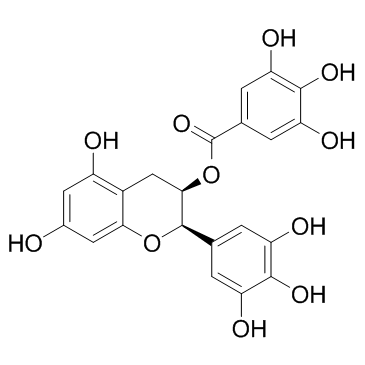 |
(-)-表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯
CAS:989-51-5 |
|
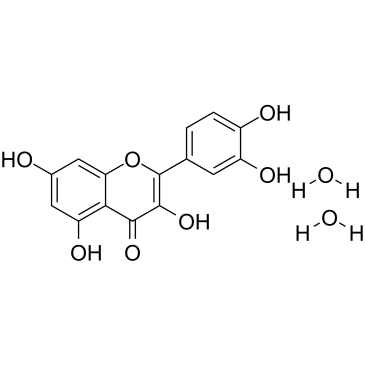 |
二水槲皮素
CAS:6151-25-3 |
|
 |
柚皮素
CAS:67604-48-2 |