| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
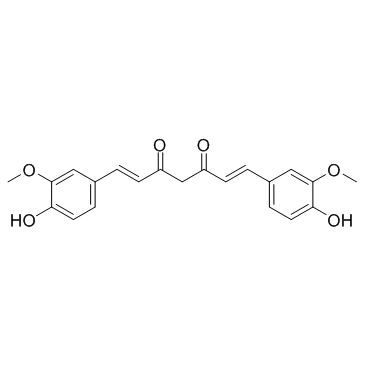 |
姜黄素
CAS:458-37-7 |
|
 |
氯化钠
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
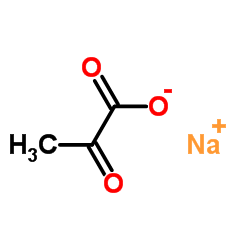 |
丙酮酸钠
CAS:113-24-6 |
|
 |
二甲基亚砜
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
L-谷氨酰胺
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
 |
4-羟乙基哌嗪乙磺酸
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
氯化钠-35cl
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
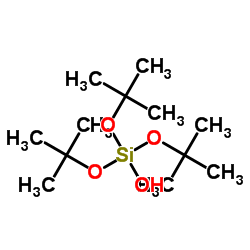 |
三(叔丁氧基)硅烷醇
CAS:18166-43-3 |
|
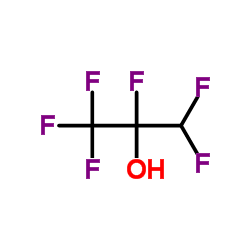 |
六氟异丙醇
CAS:920-66-1 |
|
 |
噻唑兰
CAS:298-93-1 |