| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
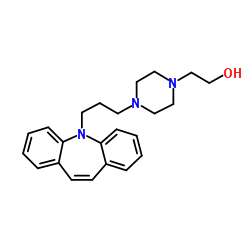 |
γ-谷氨酰转肽酶 来源于马肾脏
CAS:9046-27-9 |
|
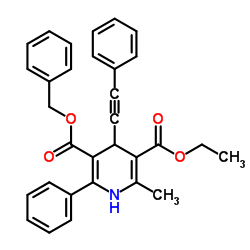 |
谷氨酸-草酰乙酸转氨酶 来源于猪心脏
CAS:9000-97-9 |