| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
硫酸
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
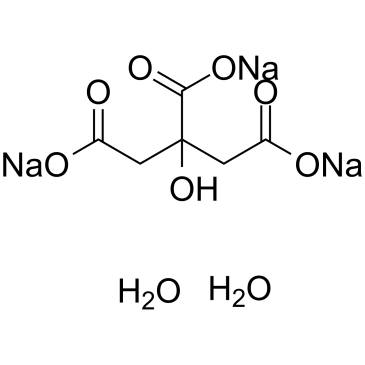 |
柠檬酸钠,二水
CAS:6132-04-3 |
|
 |
甲醇
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
甲醛
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
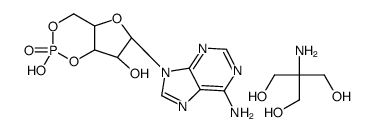 |
腺苷3',5'-环单磷酸三羟甲基氨基甲烷盐
CAS:102029-77-6 |
|
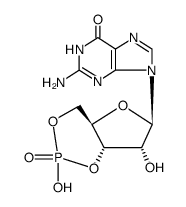 |
鸟苷3',5'-环一磷酸
CAS:7665-99-8 |
|
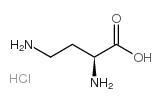 |
L-2,4-二氨基丁酸 单盐酸盐
CAS:1482-98-0 |
|
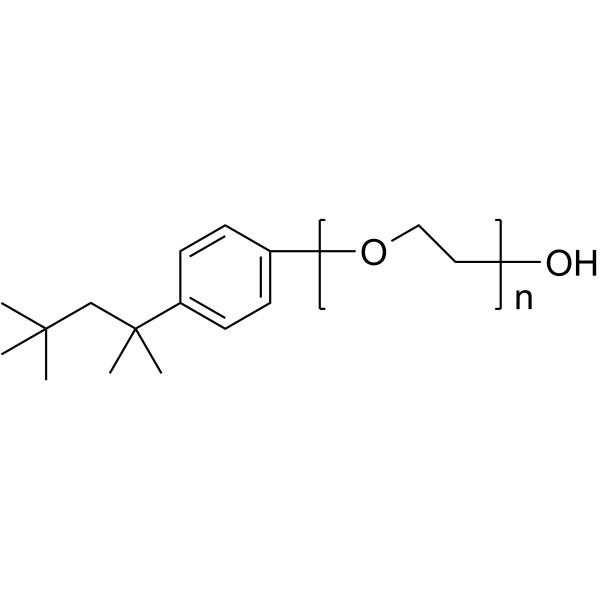 |
曲拉通X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
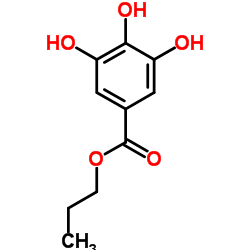 |
没食子酸丙酯
CAS:121-79-9 |
|
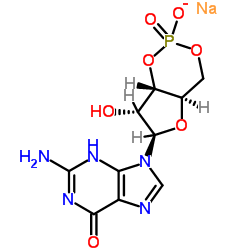 |
鸟苷3',5'-环一磷酸钠盐(cGMP)
CAS:40732-48-7 |