| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
硫酸
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
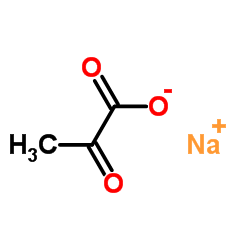 |
丙酮酸钠
CAS:113-24-6 |
|
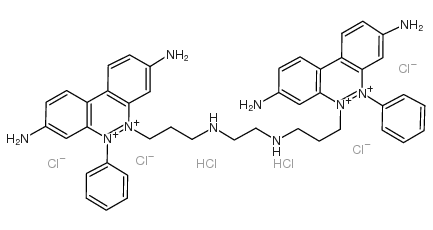 |
同二聚乙胺
CAS:61926-22-5 |
|
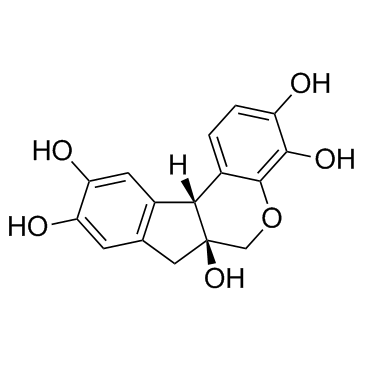 |
苏木精
CAS:517-28-2 |
|
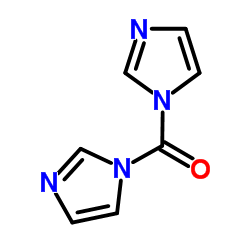 |
N,N'-羰基二咪唑(CDI)
CAS:530-62-1 |