| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
甘油
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
 |
乙二胺四乙酸
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
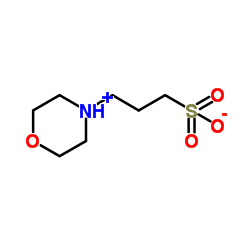 |
3-(N-吗啉)丙磺酸
CAS:1132-61-2 |
|
![N-[1-(2,3-二油酰氧基)丙基]-N,N,N-三甲基铵甲基-硫酸盐 结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/484/144189-73-1.png) |
N-[1-(2,3-二油酰氧基)丙基]-N,N,N-三甲基铵甲基-硫酸盐
CAS:144189-73-1 |