| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
甘油
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
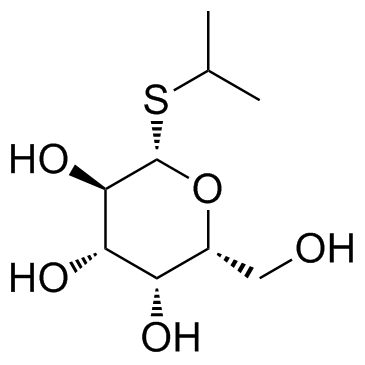 |
异丙基-β-D-硫代半乳糖苷(IPTG)
CAS:367-93-1 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
甘油
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
 |
异丙基-β-D-硫代半乳糖苷(IPTG)
CAS:367-93-1 |