Astragaloside A
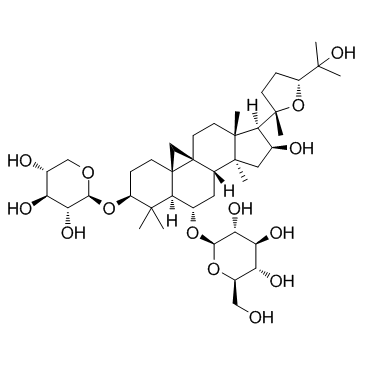
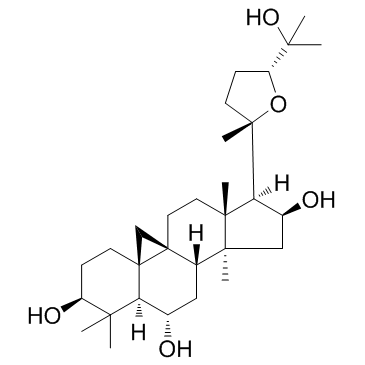
Astragaloside A structure
|
Common Name | Astragaloside A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 83207-58-3 | Molecular Weight | 784.970 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 895.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C41H68O14 | Melting Point | 284-286ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 495.5±34.3 °C | |
Use of Astragaloside AAstragaloside A is one of the major active constituents of Astragalus membranaceus in Traditional Chinese Medicine; has been widely used to treat ischemic diseases.IC50 value: Target: in vitro: AS-IV treatment promotes umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) proliferation, migration, and tube formation. AS-IV treatment also activates JAK2/STAT3 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways, and up-regulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression and nitric oxide (NO) production [1]. Administration of astragaloside IV (16, 32, and 64 μM) 1 h prior to lipopolysaccharide stimulation dose-dependently attenuated cardiac hypertrophy induced by lipopolysaccharide. Further studies demonstrated that astragaloside IV inhibited the increment of the resting intracellular free Ca2+, and its effect was similar to verapamil [2]. ASI could inhibit cells apoptosis induced by high glucose (25mmol/L) in dose-dependent and time-dependent manners. ASI also inhibited high glucose-induced expression of TGF-β1 and activation of p38 MAPK pathway at the protein level. Furthermore, ASI increased HGF production in human tubular epithelial cells [3].in vivo: the growth of tumor was suppressed by AS-IV treatment in vivo. AS-IV also could down-regulate regulatory T cells (Tregs) and up-regulate cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in vivo and in vitro[4]. As an in vivo model, mice subjected to unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) were administered AS-IV (20 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection for 7 days. AS-IV significantly alleviated renal mass loss and reduced the expression of α-smooth muscle actin, fibronectin, and collagen IV both in vitro and in vivo [5]. |
| Name | astragaloside IV |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Astragaloside A is one of the major active constituents of Astragalus membranaceus in Traditional Chinese Medicine; has been widely used to treat ischemic diseases.IC50 value: Target: in vitro: AS-IV treatment promotes umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) proliferation, migration, and tube formation. AS-IV treatment also activates JAK2/STAT3 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways, and up-regulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression and nitric oxide (NO) production [1]. Administration of astragaloside IV (16, 32, and 64 μM) 1 h prior to lipopolysaccharide stimulation dose-dependently attenuated cardiac hypertrophy induced by lipopolysaccharide. Further studies demonstrated that astragaloside IV inhibited the increment of the resting intracellular free Ca2+, and its effect was similar to verapamil [2]. ASI could inhibit cells apoptosis induced by high glucose (25mmol/L) in dose-dependent and time-dependent manners. ASI also inhibited high glucose-induced expression of TGF-β1 and activation of p38 MAPK pathway at the protein level. Furthermore, ASI increased HGF production in human tubular epithelial cells [3].in vivo: the growth of tumor was suppressed by AS-IV treatment in vivo. AS-IV also could down-regulate regulatory T cells (Tregs) and up-regulate cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in vivo and in vitro[4]. As an in vivo model, mice subjected to unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) were administered AS-IV (20 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection for 7 days. AS-IV significantly alleviated renal mass loss and reduced the expression of α-smooth muscle actin, fibronectin, and collagen IV both in vitro and in vivo [5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 895.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 284-286ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C41H68O14 |
| Molecular Weight | 784.970 |
| Flash Point | 495.5±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 784.460938 |
| PSA | 228.22000 |
| LogP | 1.96 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.621 |
| Storage condition | 2~8℃ |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|
~% 
Astragaloside A CAS#:83207-58-3 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 31, # 2 p. 716 - 722 |
|
~% 
Astragaloside A CAS#:83207-58-3 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 31, # 2 p. 709 - 715 |
|
~% 
Astragaloside A CAS#:83207-58-3 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 31, # 2 p. 698 - 708 |
|
~% 
Astragaloside A CAS#:83207-58-3 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 31, # 2 p. 698 - 708 |
|
~% 
Astragaloside A CAS#:83207-58-3 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 31, # 2 p. 698 - 708 |
|
~% 
Astragaloside A CAS#:83207-58-3 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 31, # 2 p. 698 - 708 |
|
~% 
Astragaloside A CAS#:83207-58-3 |
| Literature: Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, , vol. 31, # 2 p. 698 - 708 |
|
~% 
Astragaloside A CAS#:83207-58-3 |
| Literature: Chemistry of Natural Compounds, , vol. 40, # 1 p. 40 - 44 |
| Precursor 7 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
| Astragalus Polysaccharides |
| (3β,6α,9β,16β,20R,24S)-16,25-Dihydroxy-3-(β-D-xylopyranosyloxy)-20,24-epoxy-9,19-cyclolanostan-6-yl β-D-glucopyranoside |
| ASTRAGALOSIDE |
| ASTRAGALOSIDE IV(RG) |
| Astrasieversianin XIV |
| Astragaloside IV |
| Astragaloside A |
| β-D-Glucopyranoside, (3β,6α,9β,16β,20R,24S)-20,24-epoxy-16,25-dihydroxy-3-(β-D-xylopyranosyloxy)-9,19-cyclolanostan-6-yl |
| cyclosiversioside F |
| cyclosieversioside F |

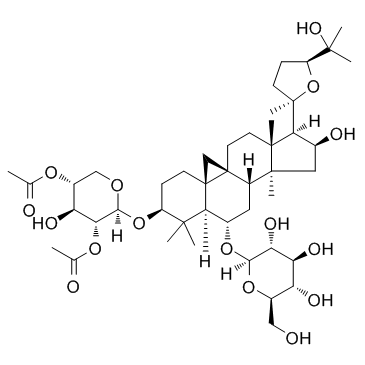
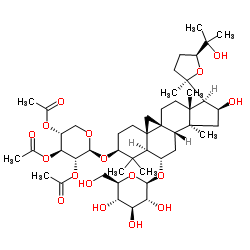
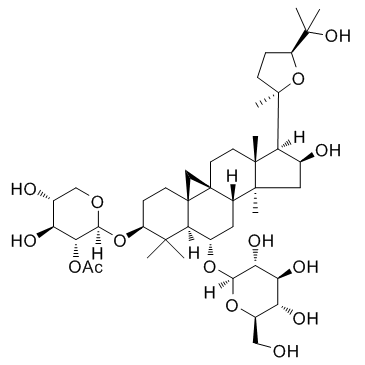
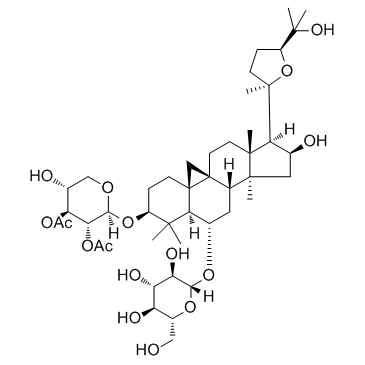

 CAS#:84605-18-5
CAS#:84605-18-5
