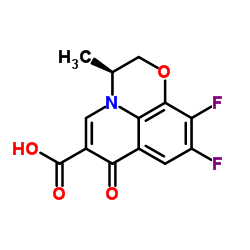
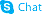138199-71-0
| Name | Levofloxacin Hemihydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Levofloxacin
7H-1,4-Oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic acid, 9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-, (3S)-, hydrate (1:1) (3S)-9-Fluoro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7H-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic acid hydrate (1:1) MFCD03265511 Levofloxacin hemihydrate (S)-9-Fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido(1,2,3-de)-1,4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid hydrate (2:1) Levofloxacin hydrate |
| Description | Levofloxacin hydrate is an antibacterial agent that inhibits the supercoiling activity of bacterial DNA gyrase, halting DNA replication.Target: AntibacterialLevofloxacin reduced bacterial load compared with placebo by 4.9-fold (95% confidence interval, 1.4-25.7; P=0.02) at day 7 but had no effect at any point on any marker of neutrophilic airway inflammation. In patients with a baseline bacterial load of more than 10(6) cfu/mL, levofloxacin treatment was associated with a 26.5% (95% confidence interval, 1.8%-51.3%; P=0.04) greater reduction in the percentage neutrophil count compared with placebo at day 7 [1]. Levofloxacin was found to significantly improve the clinical and microbiological parameters in CP individuals [2]. A 30-day course of levofloxacin does not significantly improve BK viral load reduction or allograft function when used in addition to overall reduction of immunosuppression [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.48g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 571.5ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 214-216°C |
| Molecular Formula | C18H20FN3O4.0.5H2O |
| Molecular Weight | 370.38 |
| PSA | 84.24000 |
| LogP | 1.48260 |
| Vapour Pressure | 6.7E-14mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H317-H334-H361d-H362 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P263-P280-P342 + P311 |
| Hazard Codes | N |
| Risk Phrases | 50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~% 
138199-71-0 |
| Literature: US2003/130507 A1, ; |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |