2-Deoxy-D-glucose-13C
Modify Date: 2025-08-21 09:48:21
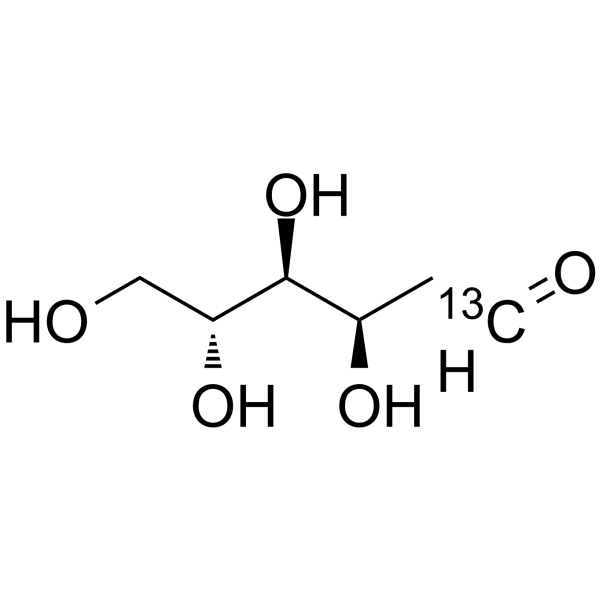
2-Deoxy-D-glucose-13C structure
|
Common Name | 2-Deoxy-D-glucose-13C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 201612-55-7 | Molecular Weight | 165.14900 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of 2-Deoxy-D-glucose-13C2-Deoxy-D-glucose-13C is the 13C labeled 2-Deoxy-D-glucose. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose is a glucose analog that acts as a competitive inhibitor of glucose metabolism, inhibiting glycolysis via its actions on hexokinase[1][2]. |
| Name | 2-deoxy-d-[1-13c]arabino-hexose |
|---|
| Description | 2-Deoxy-D-glucose-13C is the 13C labeled 2-Deoxy-D-glucose. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose is a glucose analog that acts as a competitive inhibitor of glucose metabolism, inhibiting glycolysis via its actions on hexokinase[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 165.14900 |
| Exact Mass | 165.07200 |
| PSA | 90.15000 |
| InChIKey | PMMURAAUARKVCB-UPKQYVFDSA-N |
| SMILES | OCC1OC(O)CC(O)C1O |