3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid
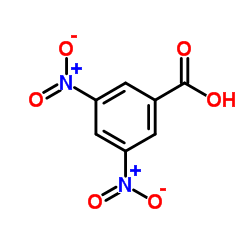
3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid structure
|
Common Name | 3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 99-34-3 | Molecular Weight | 212.117 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 395.5±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H4N2O6 | Melting Point | 204-206 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 179.2±13.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | 3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 395.5±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 204-206 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H4N2O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 212.117 |
| Flash Point | 179.2±13.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 212.006943 |
| PSA | 128.94000 |
| LogP | 1.69 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.658 |
| Stability | Stable. Contact with strong bases may lead to fire. Incompatible with strong bases, strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | 1350 mg/L (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335-H413 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | F:Flammable;Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R11;R22;R36/37/38;R68 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S16 |
| RIDADR | UN1325 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DG9140700 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 4.1 |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916399090 other aromatic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
A method for rapid screening of ketone biotransformations: detection of whole cell Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase activity.
Enzyme Microb. Technol. 50(2) , 101-6, (2012) A method for screening of ketone biotransformations was developed and applied to the identification of Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase (BVMO) activity. The method was based on the formation of a purple ... |
|
|
Electronic, infrared, and 1HNMR spectral studies of the novel charge-transfer complexes of o-tolidine and p-toluidine with alternation pi-acceptors (3,5-dinitro benzoic acid and 2,6-dichloroquinone-4-chloroimide) in CHCl3 solvent.
Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 64(3) , 778-88, (2006) The rapid interaction between o-tolidine and p-toluidine (pi-donors) with the pi-acceptors, e.g., 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (DNB) and 2,6-dichloroquinone-4-chloroimide (DCQ) results in the formation of ... |
|
|
Method development in quantitative NMR towards metrologically traceable organic certified reference materials used as (31)P qNMR standards.
Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407 , 3115-3123, (2015) Quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance (qNMR) spectroscopy is employed by an increasing number of analytical and industrial laboratories for the assignment of content and quantitative determination o... |
| Benzoic acid, 3,5-dinitro- |
| 3,5-Dinitro Benzoic Acid |
| Dinitrobenzoic acid |
| WNR CVQ ENW |
| Benzoic acid,3,5-dinitro |
| 3,5-di-NO2PhCOOH |
| DNBA |
| 3-Carboxy-1,5-dinitrobenzene |
| EINECS 202-751-1 |
| 3,5-Dinitro-benzoic acid |
| MFCD00007253 |
 CAS#:65-85-0
CAS#:65-85-0 CAS#:2702-58-1
CAS#:2702-58-1 CAS#:618-71-3
CAS#:618-71-3 CAS#:54619-90-8
CAS#:54619-90-8 CAS#:79239-16-0
CAS#:79239-16-0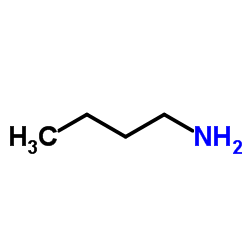 CAS#:109-73-9
CAS#:109-73-9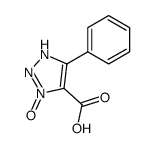 CAS#:879544-86-2
CAS#:879544-86-2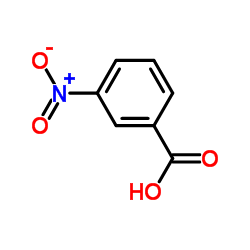 CAS#:121-92-6
CAS#:121-92-6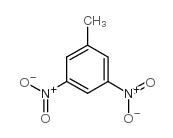 CAS#:618-85-9
CAS#:618-85-9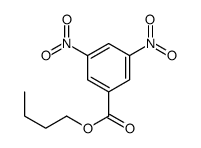 CAS#:10478-02-1
CAS#:10478-02-1 CAS#:10477-99-3
CAS#:10477-99-3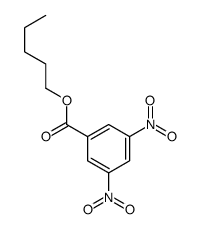 CAS#:10478-03-2
CAS#:10478-03-2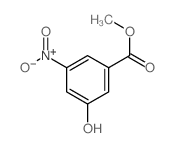 CAS#:55076-32-9
CAS#:55076-32-9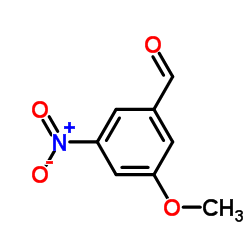 CAS#:354512-22-4
CAS#:354512-22-4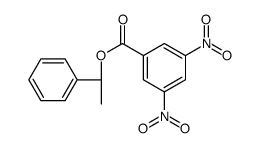 CAS#:3205-18-3
CAS#:3205-18-3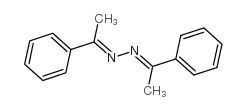 CAS#:729-43-1
CAS#:729-43-1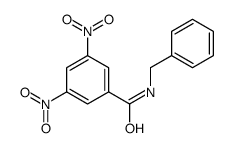 CAS#:14401-98-0
CAS#:14401-98-0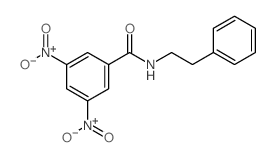 CAS#:14401-99-1
CAS#:14401-99-1 CAS#:90390-46-8
CAS#:90390-46-8
