FPH2
Modify Date: 2025-08-24 14:07:27
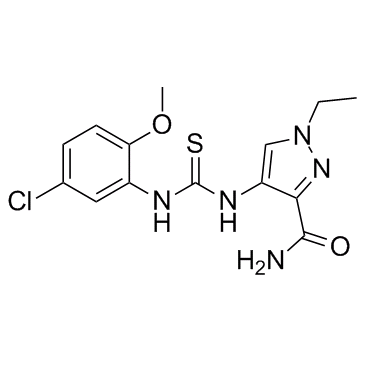
FPH2 structure
|
Common Name | FPH2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 957485-64-2 | Molecular Weight | 353.82700 | |
| Density | 1.45±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H16ClN5O2S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of FPH2FPH2 induces of functional proliferation of primary human hepatocytes and may lead to the development of new therapeutics for liver diseases. |
| Name | 1H-Pyrazole-3-carboxamide, 4-[[[(5-chloro-2-methoxyphenyl)amino]thioxomethyl]amino]-1-ethyl- |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | FPH2 induces of functional proliferation of primary human hepatocytes and may lead to the development of new therapeutics for liver diseases. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | FPH2 induces functional proliferation of hepatocytes in vitro, and thus may be useful for expanding mature human primary hepatocytes. FPH1 and FPH2 can increase in hepatocyte nuclei count and/or elevate the number of nuclei undergoing mitosis during primary screening, and these effects on hepatocytes are concentration dependent. Cells treated with FPH1 and FPH2 also maintain their liver-specific functions. Over 7 days, FPH2 induces hepatocyte doublings at a rate that is consistent with reported liver regeneration kinetics in vivo[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.45±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H16ClN5O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 353.82700 |
| Exact Mass | 353.07100 |
| PSA | 126.29000 |
| LogP | 3.31910 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Water Solubility | Practically insoluble (0.046 g/L) (25 ºC) |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
| FPH2 |
| 4-[[[(5-Chloro-2-methoxyphenyl)amino]thioxomethyl]amino]-1-ethyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide |
| BRD-9424 |