Diisobutyl phthalate

Diisobutyl phthalate structure
|
Common Name | Diisobutyl phthalate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 84-69-5 | Molecular Weight | 278.344 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 295.3±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H22O4 | Melting Point | -64 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 153.9±7.9 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | diisobutyl phthalate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 295.3±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -64 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C16H22O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 278.344 |
| Flash Point | 153.9±7.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 278.151794 |
| PSA | 52.60000 |
| LogP | 4.46 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.497 |
| InChIKey | MGWAVDBGNNKXQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C)COC(=O)c1ccccc1C(=O)OCC(C)C |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble |
| Freezing Point | -50℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H360Df-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P273-P308 + P313-P391-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R50/53;R62;R63 |
| Safety Phrases | S60-S61-S36/37 |
| RIDADR | UN 3082 9/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | TI1225000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 9 |
| HS Code | 29173400 |
|
~% 
Diisobutyl phthalate CAS#:84-69-5 |
| Literature: US2091241 , ; |
|
~% 
Diisobutyl phthalate CAS#:84-69-5 |
| Literature: Archiv der Pharmazie (Weinheim, Germany), , vol. 287, p. 457 |
| HS Code | 2917349000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2917349000 other esters of orthophthalic acid。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Analysis of phthalates in milk and milk products by liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole Orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1362 , 110-8, (2014) A new analytical method was developed and validated for simultaneous analysis of 27 phthalates in milk and milk products. Response surface methodology was employed to optimize a quick, easy, cheap, ef... |
|
|
Rapid screening and identification of multi-class substances of very high concern in textiles using liquid chromatography-hybrid linear ion trap orbitrap mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1386 , 22-30, (2015) A new analytical method was established and validated for the analysis of 19 substances of very high concern (SVHCs) in textiles, including phthalic acid esters (PAEs), organotins (OTs), perfluorochem... |
|
|
Development and application of a non-targeted extraction method for the analysis of migrating compounds from plastic baby bottles by GC-MS.
Food Addit. Contam. Part A. Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 31(12) , 2090-102, (2014) In 2011, the European Union prohibited the production of polycarbonate (PC) baby bottles due to the toxic effects of the PC monomer bisphenol-A. Therefore, baby bottles made of alternative materials, ... |
| Phthaloyl dichloride |
| MFCD01861606 |
| EINECS 201-553-2 |
| Phthalyl chloride |
| bis(2-methylpropyl) benzene-1,2-dicarboxylate |
| Phthalic dichloride |
| 1,2-Benzenedicarbonyl dichloride |
| tetraphthaloyl chloride |
| Phthalic acid dichloride |
| diisobutyl 1,2-benzenedicarboxylate |
| 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methylpropyl) ester |
| di-l-butyl phthalate (DIBP) |
| Diisobutyl phthalate |
| phthaloyl chloride |
| Phthalyl dichloride |
| benzene-1,2-dicarbonyl dichloride |
| Phthalic chloride |

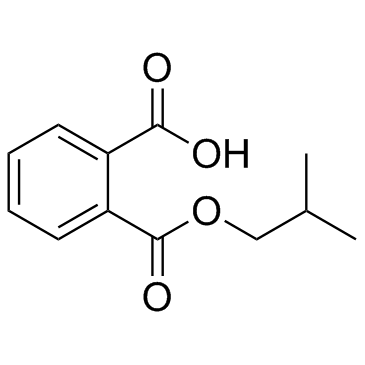 CAS#:30833-53-5
CAS#:30833-53-5
