Lead sulfate
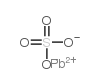
Lead sulfate structure
|
Common Name | Lead sulfate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7446-14-2 | Molecular Weight | 303.26300 | |
| Density | 6.2 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | O4PbS | Melting Point | 1170 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | lead(ii) sulfate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 6.2 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 1170 °C |
| Molecular Formula | O4PbS |
| Molecular Weight | 303.26300 |
| Exact Mass | 303.92800 |
| PSA | 88.64000 |
| Stability | Stable. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H332-H360Df-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P260-P280-P301 + P312 + P330-P308 + P313 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T: Toxic;N: Dangerous for the environment; |
| Risk Phrases | R61;R20/22;R33;R50/53;R62 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45-S60-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | OG4375000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
|
Chemical transformations of lead compounds under humid conditions: implications for bioaccessibility.
Environ. Geochem. Health 35(1) , 153-9, (2013) This short communication documents chemical transformations caused by weathering of two Pb compounds that commonly occur in house dust. Chamber experiments were designed to simulate humid indoor envir... |
|
|
Phosphate-induced lead immobilization from different lead minerals in soils under varying pH conditions.
Environ. Pollut. 152(1) , 184-92, (2008) This study investigated phosphate-induced lead immobilization from different Pb minerals in soils under varying pHs. Four soils were used, including one Pb-contaminated soil (NC-Soil) and three soils ... |
|
|
The effects of lead sulfate on new sealed lead acid batteries.
J. Emerg. Med. 18(3) , 305-9, (2000) Emergency Medical Services (EMS) rely on batteries to power external cardiac defibrillators. While maintenance protocols should be followed to ensure that batteries possess adequate capacity to power ... |
| EINECS 231-198-9 |
| Anglislite |
| MFCD00011166 |
| Anglesite |
| milkwhite |
| Lead dross |
| Bleisulfat |
| fastwhite |

