Dazopride
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 17:12:17
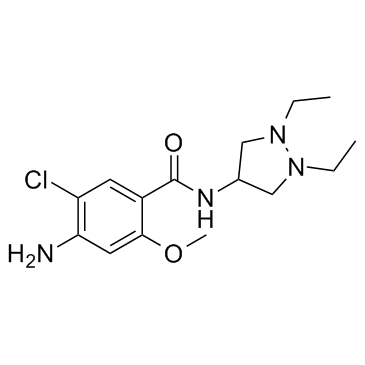
Dazopride structure
|
Common Name | Dazopride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 70181-03-2 | Molecular Weight | 326.82200 | |
| Density | 1.27g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H23ClN4O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of DazoprideDazopride is an antiemetic agent. |
| Name | 4-amino-5-chloro-N-(1,2-diethylpyrazolidin-4-yl)-2-methoxybenzamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dazopride is an antiemetic agent. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Dazopride (0.3 mg/kg) produces significant enhancement of gastric evacuation and is approximately six times more potent than metoclopramide in gastric evacuation assay. Dazopride (0.3-10.0 mg/kg, i.v.) produces a dose-related increase in antral motility primarily by increasing the amplitude of antral contractions in three conscious dogs. Dazopride significantly reduces the emetic frequency from that of the control group[1]. Dazopride (5 mg/kg, i.p.) antagonises the tetralin-induced emesis in all animals, but fails to antagonise the response at 0.25-2.5 mg/kg. Dazopride fails to modify cisplatin-induced emesis at 0.1 mg/kg (i.v,) although a larger dose of 1.0 mg/kg abolishes or attenuates the response and 5.0 mg/kg of dazopride antagonises the development ofemesis in all animals[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.27g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H23ClN4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 326.82200 |
| Exact Mass | 326.15100 |
| PSA | 70.83000 |
| LogP | 2.44950 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.6 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
|
~% 
Dazopride CAS#:70181-03-2 |
| Literature: A. H. Robins Company, Inc. Patent: US4207327 A1, 1980 ; |
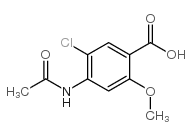
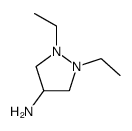
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| Dazopride |
| Dazopride [INN] |
| Dazopridum |
| 4-amino-5-chloro-N-(1,2-diethyl-pyrazolidin-4-yl)-2-methoxy-benzamide |
| Dazoprida |
| 4-amino-5-chloro-2-methoxy-N-(1,2-diethyl-4-pyrazolidinyl)benzamide |
| UNII-CV07VSP2G8 |