| Description |
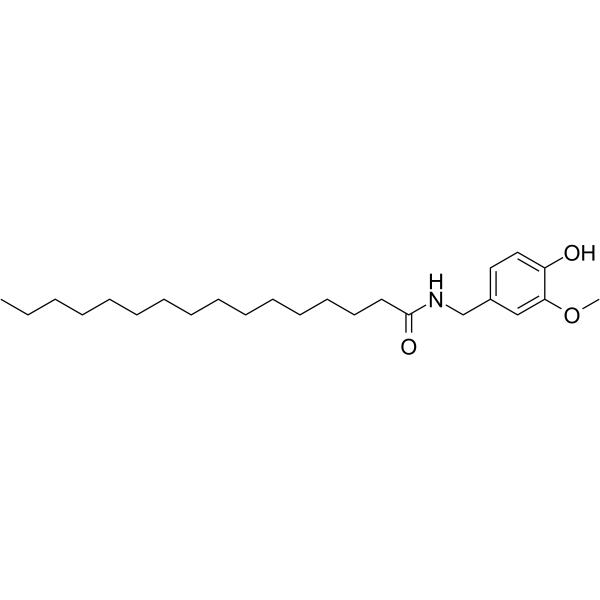
Palvanil is a capsaicin analogue, shows strong desensitizing capability against the TRPV1 receptor. Palvanil shows anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammation effects[1][2].
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| In Vitro |
Palvanil (0.1-1000 nM; 0-300 min) leads to calcium increasment in intracellular[1]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: HEK-293 cells Concentration: 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 50, 100 and 1000 nM Incubation Time: 0-300 min Result: Produced a dose-dependent increase in intracellular calcium with a EC50 of 0.65 nM.
|
| In Vivo |
Palvanil (Subcutaneous injection; 1 or 10 mg/kg; once) treatment shows hypothermic effect[2]. Palvanil (Intraperitoneal injection; 100 μL (15 nM) per mouse; once) treatment reduces capsaicin-induced bronchoconstriction[2]. Palvanil (Intravenous injection; 0.5, 0.75, and 1 mg/kg; once) treatment shows antinociceptive effects on formalin-induced nocifensive behavior[2]. Palvanil (Intravenous injection; 0.5, 0.75, and 1 mg/kg; once) treatment inhibits carrageenan-induced inflammation[2]. Palvanil (Intravenous injection; 0.5 and 1 mg/kg; once daily; 7 days) reduces mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in SNI mice[2]. Animal Model: Male CD-1 mice[2] Dosage: 1 or 10 mg/kg Administration: Subcutaneous injection; 1 or 10 mg/kg; once Result: Led to a slight and short lasting hypothermic effect, produced late hyperthermia. Animal Model: Female BALB/C mice[2] Dosage: 100 μL (15 nM) per mouse Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; 100 μL (15 nM) per mouse; once Result: Induced a significantly lower bronchoconstriction (from 0.47 to 0.605 cm H2O/L/s). Animal Model: Male CD-1 mice received formalin[2] Dosage: 0.5, 0.75, and 1 mg/kg Administration: Intravenous injection; 0.5, 0.75, and 1 mg/kg; once Result: Reduced the second phase of formalin-induced nociceptive behaviour in a dose-dependent manner. Animal Model: Male C57BL/6J mice with acute inflammation induced by carrageenan[2] Dosage: 2.5 mg/kg Administration: Intravenous injection; 2.5 mg/kg; once Result: Reduced the volume of the oedema in the ipsilateral hind paw (64%). Animal Model: Male CD-1 mice[2] Dosage: 0.5 and 1 mg/kg Administration: Intravenous injection; 0.5 and 1 mg/kg; once daily; 7 days Result: Reduced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia at 3 and 7 days after nerve injury in a dose-dependent manner.
|
| References |
[1]. Luciano De Petrocellis, et al. N-palmitoyl-vanillamide (palvanil) is a non-pungent analogue of capsaicin with stronger desensitizing capability against the TRPV1 receptor and anti-hyperalgesic activity. Pharmacol Res. 2011 Apr;63(4):294-9. [2]. Livio Luongo, et al. Palvanil, a non-pungent capsaicin analogue, inhibits inflammatory and neuropathic pain with little effects on bronchopulmonary function and body temperature. Pharmacol Res. 2012 Sep;66(3):243-50.
|