Norverapamil hydrochloride
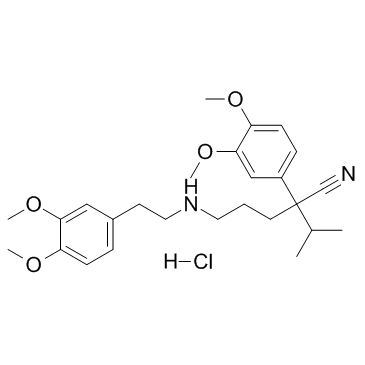
Norverapamil hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Norverapamil hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 67812-42-4 | Molecular Weight | 477.04 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H37ClN2O4 | Melting Point | 155-160℃ dec. | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of Norverapamil hydrochlorideNorverapamil is a calcium channel blocker, it is the main active metabolite of verapamil.In vitro: Norverapamil is similarly effective as verapamil at inhibiting isoniazid and rifampicin tolerance and killing of intracellular M. tuberculosis in the absence of other drugs. norverapamil, also inhibits macrophage-induced tolerance and achieves similar serum levels to verapamil.[1] Norverapamil (NOR) is the major metabolite and shows approximately 20% of the efficacy of VER with regard to the vasodilation effect, but shows no antiarrhythmic activity. [2] Verapamil and its major metabolite norverapamil were identified to be both mechanism-based inhibitors and substrates of CYP3A and reported to have non-linear pharmacokinetics in clinic. [3] |
| Name | 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)ethylamino]-2-propan-2-ylpentanenitrile,hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Norverapamil is a calcium channel blocker, it is the main active metabolite of verapamil.In vitro: Norverapamil is similarly effective as verapamil at inhibiting isoniazid and rifampicin tolerance and killing of intracellular M. tuberculosis in the absence of other drugs. norverapamil, also inhibits macrophage-induced tolerance and achieves similar serum levels to verapamil.[1] Norverapamil (NOR) is the major metabolite and shows approximately 20% of the efficacy of VER with regard to the vasodilation effect, but shows no antiarrhythmic activity. [2] Verapamil and its major metabolite norverapamil were identified to be both mechanism-based inhibitors and substrates of CYP3A and reported to have non-linear pharmacokinetics in clinic. [3] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Melting Point | 155-160℃ dec. |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H37ClN2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 477.04 |
| LogP | 2.02400 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
|
Verapamil, and its metabolite norverapamil, inhibit macrophage-induced, bacterial efflux pump-mediated tolerance to multiple anti-tubercular drugs.
J. Infect. Dis. 210(3) , 456-66, (2014) Drug tolerance likely represents an important barrier to tuberculosis treatment shortening. We previously implicated the Mycobacterium tuberculosis efflux pump Rv1258c as mediating macrophage-induced ... |
|
|
Application of permeability-limited physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models: part II - prediction of P-glycoprotein mediated drug-drug interactions with digoxin.
J. Pharm. Sci. 102(9) , 3161-73, (2013) Digoxin is the recommended substrate for assessment of P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated drug-drug interactions (DDIs) in vivo. The overall aim of our study was to investigate the inhibitory potential of... |
|
|
Stereoselective CZE method for analysis of verapamil and norverapamil in human plasma.
Acta Pol. Pharm. 70(3) , 395-401, (2013) A stereospecific capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) method was developed for the determination of verapamil (VER) and its main metabolite norverapamil (NOR) in human plasma. Optimal temperature, cyc... |
| N-Nor-(+/-)-verapamil hydrochloride |
| Nor Verapamil Hydrochloride |
| Norverapamil hydrochloride |
| Norverapamil (hydrochloride) |