DL-Leucine (2-13C)
Modify Date: 2025-08-27 15:01:18
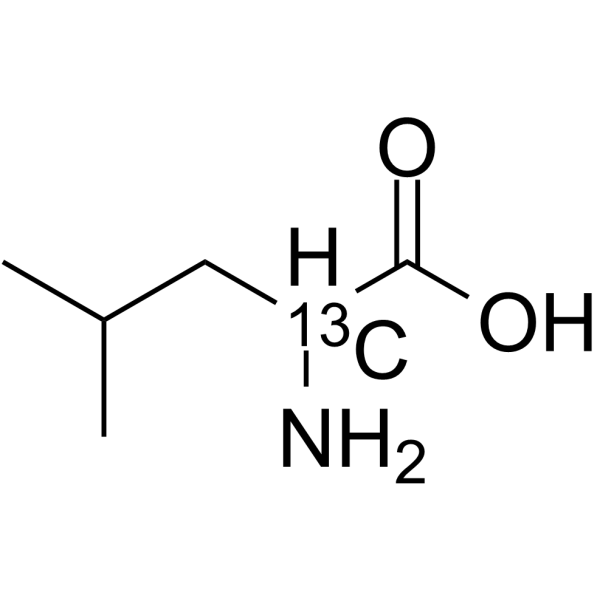
DL-Leucine (2-13C) structure
|
Common Name | DL-Leucine (2-13C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 65792-32-7 | Molecular Weight | 132.166 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO2 | Melting Point | 293-296ºC (subl.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of DL-Leucine (2-13C)(±)-Leucine-13C (DL-Leucine-13C) is the 13C-labeled (±)-Leucine. (±)-Leucine (DL-Leucine), an isomer of Leucine, chemosterilant and dietary additive. (±)-Leucine inhibits growth of Escherichia coli HfrH by 92.08%[1]. |
| Name | 2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | (±)-Leucine-13C (DL-Leucine-13C) is the 13C-labeled (±)-Leucine. (±)-Leucine (DL-Leucine), an isomer of Leucine, chemosterilant and dietary additive. (±)-Leucine inhibits growth of Escherichia coli HfrH by 92.08%[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 293-296ºC (subl.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 132.166 |
| Exact Mass | 132.097977 |
| PSA | 63.32000 |
| LogP | 1.14470 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.463 |
| InChIKey | ROHFNLRQFUQHCH-HOSYLAQJSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(N)C(=O)O |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
| (2-C)Leucine |
| MFCD00144180 |
| DL-Leucine-2-13C |
| Leucine-2-C |