Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC acetate salt
Modify Date: 2025-08-20 17:27:24
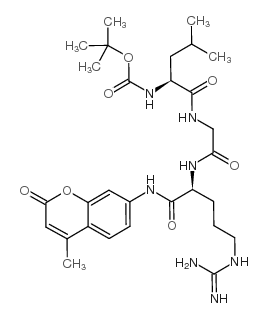
Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC acetate salt structure
|
Common Name | Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC acetate salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 65147-09-3 | Molecular Weight | 601.69400 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C29H43N7O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC acetate saltBoc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC is a fluorogenic AMC substrate for the convertases. Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC can be used in enzymatic assays[1][2]. |
| Name | Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC is a fluorogenic AMC substrate for the convertases. Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC can be used in enzymatic assays[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | To demonstrate the presence in the abdominal gland of proteolytic enzymes capable of generating Sodefrin, an enzymatic assay was developed using Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC as synthetic substrate. A crude extract of the abdominal gland hydrolyzed Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC to liberate 7-amino-4- methylcoumarin, suggesting that enzymes that generate sodefrin from its precursor molecule are present in the gland. The activity in the extract for cleaving Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC is optimal at pH 9.0 and 45 ℃[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C29H43N7O7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 601.69400 |
| Exact Mass | 601.32200 |
| PSA | 217.74000 |
| LogP | 4.28020 |
| InChIKey | DLAQYOHJZUTWDJ-SFTDATJTSA-N |
| SMILES | Cc1cc(=O)oc2cc(NC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)ccc12 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| tert-butyl N-[1-[[2-[[5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1-[(4-methyl-2-oxochromen-7-yl)amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]carbamate |