Carvedilol phosphate
Modify Date: 2024-01-05 16:22:11
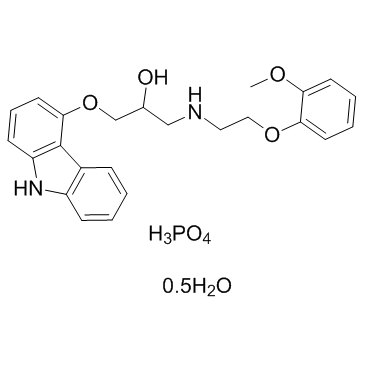
Carvedilol phosphate structure
|
Common Name | Carvedilol phosphate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 610309-89-2 | Molecular Weight | 513.48 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 655.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H26N2O4.H3PO4.1/2H2O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 350.1ºC | |
Use of Carvedilol phosphateCarvedilol is a non-selective beta blocker/alpha-1 blocker with an IC50 of 3.8 μM for inhibition of LDL oxidation.IC50 Value: 3.8 μM ( inhibition of LDL oxidation)Target: beta Adrenergic ReceptorCarvedilol is a nonselective-blocking agent and is used in the treatment of hypertension and angina pectoris. As a third-generation β-adrenergic blocker (β-blocker), Carvedilol is able to reverse cardiac structural remodeling. Recentresults demonstrated that the effect caused by Carvedilol on cardiac remodeling is largely dependent on endogenous NO. |
| Name | 1-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethylamino]propan-2-ol,phosphoric acid,hydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Carvedilol is a non-selective beta blocker/alpha-1 blocker with an IC50 of 3.8 μM for inhibition of LDL oxidation.IC50 Value: 3.8 μM ( inhibition of LDL oxidation)Target: beta Adrenergic ReceptorCarvedilol is a nonselective-blocking agent and is used in the treatment of hypertension and angina pectoris. As a third-generation β-adrenergic blocker (β-blocker), Carvedilol is able to reverse cardiac structural remodeling. Recentresults demonstrated that the effect caused by Carvedilol on cardiac remodeling is largely dependent on endogenous NO. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[2]. Stafylas PC, et al. Carvedilol in hypertension treatment. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008;4(1):23-30. |
| Boiling Point | 655.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H26N2O4.H3PO4.1/2H2O |
| Molecular Weight | 513.48 |
| Flash Point | 350.1ºC |
| PSA | 172.54000 |
| LogP | 3.13600 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| 2-Propanol, 1-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-[[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]-, phosphate, hydrate (2:2:1) (salt) |
| Carvedilol phosphate hydrate (JAN) |
| Carvedilol phosphate hemihydrate |
| Coreg CR (TN) |
| 1-(9H-Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-{[2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino}-2-propanol phosphate hydrate (2:2:1) |
| Carvedilol phosphate |
| Carvedilol (phosphate hemihydrate) |