thiodicarb
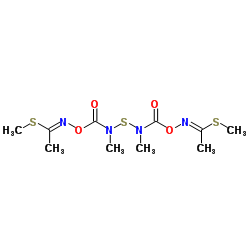
thiodicarb structure
|
Common Name | thiodicarb | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 59669-26-0 | Molecular Weight | 354.469 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 433.8±28.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H18N4O4S3 | Melting Point | 168-172°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 216.2±24.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of thiodicarbThiodicarb is a carbamate insecticide used to control flies in animal and poultry houses and dairies. Thiodicarb is metabolized into methomyl in animals and plants, and subsequently degraded into carbon dioxide and acetonitrile[1]. |
| Name | thiodicarb |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Thiodicarb is a carbamate insecticide used to control flies in animal and poultry houses and dairies. Thiodicarb is metabolized into methomyl in animals and plants, and subsequently degraded into carbon dioxide and acetonitrile[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Thiodicarb exhibit both oral and contact activity against major Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Diptera, and Hemiptera pests, which affect cotton, soya beans, maize, vines, fruit, and vegetables[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 433.8±28.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 168-172°C |
| Molecular Formula | C10H18N4O4S3 |
| Molecular Weight | 354.469 |
| Flash Point | 216.2±24.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 354.049011 |
| PSA | 159.70000 |
| LogP | 1.52 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.575 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301-H330-H400 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P273-P284-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+: Very toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R25 |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S36/37-S45 |
| RIDADR | 2757 |
| RTECS | KJ4301050 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
|
Nematicides enhance growth and yield of rotylenchulus reniformis resistant cotton genotypes.
J. Nematol. 46(4) , 365-75, (2015) Rotylenchulus reniformis resistant LONREN-1×FM966 breeding lines developed at Auburn University have demonstrated that the nematode resistance is accompanied by severe stunting, limited growth, and lo... |
|
|
Tobacco budworm P-glycoprotein: biochemical characterization and its involvement in pesticide resistance.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1291(2) , 155-62, (1996) Since pesticides have been shown to interact with P-glycoprotein (P-gp), the purpose of this study was to examine the possible role of P-gp in pesticide resistance in the tobacco budworm (Heliothis vi... |
|
|
Thiodicarb and methomyl tissue distribution in a fatal multiple compounds poisoning.
J. Forensic Sci. 53(2) , 499-502, (2008) Thiodicarb is a nonsystemic carbamate insecticide whose acetylcholinesterase activity is related to its main methomyl degradation product. A 40-year-old woman was found dead in her car. Empty packages... |
| semevin |
| LARVIN |
| SKIPPER |
| CHIPCO |
| NIVRAL |
| dimethyl N,N’-[thiobis[(methylimino)carbonyloxy]]bis[ethanimidothioate] |
| (3EZ,12EZ)-3,7,9,13-tetramethyl-5,11-dioxa-2,8,14-trithia-4,7,9,12-tetraazapentadeca-3,12-diene-6,10-dione |
| lepicron |
| MFCD00145401 |
| Thiodicarb |
| EINECS 261-848-7 |

