cymoxanil

cymoxanil structure
|
Common Name | cymoxanil | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 57966-95-7 | Molecular Weight | 198.179 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H10N4O3 | Melting Point | 160-161ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 100 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of cymoxanilCymoxanil is a fungicidal against plant diseases caused by fungi belonging to the Perenosporales[1]. |
| Name | cymoxanil |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cymoxanil is a fungicidal against plant diseases caused by fungi belonging to the Perenosporales[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Fungal[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 160-161ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C7H10N4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 198.179 |
| Flash Point | 100 °C |
| Exact Mass | 198.075287 |
| PSA | 103.58000 |
| LogP | 0.67 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.537 |
| InChIKey | XERJKGMBORTKEO-VZUCSPMQSA-N |
| SMILES | CCNC(=O)NC(=O)C(C#N)=NOC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H317-H361fd-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P273-P280-P308 + P313-P333 + P313-P391 |
| Target Organs | Blood, thymus |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R43;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S36/37-S60-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 |
| RTECS | AB5957000 |
| HS Code | 2926909038 |
| HS Code | 2926909038 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2926909038 fenoxanil Educational tariff:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Regulatory conditions:S(Registration certificate of import and export) Lowest tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Dissipation and residue of metalaxyl and cymoxanil in pepper and soil.
Environ. Monit. Assess. 186(8) , 5307-13, (2014) A simple and accurate method of determining metalaxyl and cymoxanil in pepper and soil was developed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detection. The limits of detection were... |
|
|
Detection of resistance to fungicides, mating types and fitness of Phytophthora infestans in Hebei, China.
Meded. Rijksuniv. Gent. Fak. Landbouwkd. Toegep. Biol. Wet. 67(2) , 307-14, (2002) In vitro, isolates resistant to metalaxyl (M) and oxadixyl (O) of Phytophthora infestans were 11.2% of 62 isolates from potato and tomato in Hebei Province, mean resistance factor was 15,022 fold and ... |
|
|
Development of a gas chromatographic method for fungicide cymoxanil analysis in dried hops.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 49(2) , 570-3, (2001) An analytical method for detecting cymoxanil [2-cyano-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-2-(methoxyimino)acetamide] residues in dried hops was developed utilizing liquid-liquid partitioning, automated gel perme... |
| Cymoxanil |
| 1-[(EZ)-2-cyano-2-methoxyiminoacetyl]-3-ethylurea |
| CURZATE |
| cymoxyanil |
| dpx3217m |
| PULSAN |
| RIFLE XG |
| (2Ξ)-2-cyano-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetamide |
| 1-(2-Cyano-2-methoxyiminoacetyl)-3-ethylurea |
| 2MVMVYCN&UNO1 |
| EINECS 261-043-0 |
| MANEX C-8 |
| MFCD00137381 |
| 2-Cyano-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-2-(methoxyimino)acetamide |
| CIMOXPRON |
| Acetamide, 2-cyano-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-2-(methoxyimino)- |
| 2-Cyano-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetamide |
| cymoxanil [ANSI] |
| DPX 3217 |
 CAS#:41078-06-2
CAS#:41078-06-2 CAS#:41078-09-5
CAS#:41078-09-5 CAS#:77-78-1
CAS#:77-78-1 CAS#:57012-86-9
CAS#:57012-86-9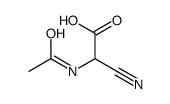 CAS#:89188-25-0
CAS#:89188-25-0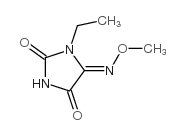 CAS#:71342-67-1
CAS#:71342-67-1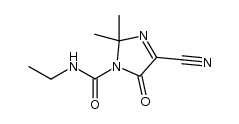 CAS#:1055979-74-2
CAS#:1055979-74-2
