celiprolol
Modify Date: 2025-08-19 18:52:13

celiprolol structure
|
Common Name | celiprolol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56980-93-9 | Molecular Weight | 379.494 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 586.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H33N3O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 308.5±30.1 °C | |
Use of celiprololCeliprolol (REV 5320) is a potent, cardioselective and orally active β1-andrenoceptor r antagonist with partial β2 agonist activity, with Ki values of 0.14-8.3 μM. Celiprolol has antihypertensive and antianginal activity, and can be used for the research of cardiovascular disease such as high blood pressure[1][4]. |
| Name | 3-[3-acetyl-4-[3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy]phenyl]-1,1-diethylurea |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Celiprolol (REV 5320) is a potent, cardioselective and orally active β1-andrenoceptor r antagonist with partial β2 agonist activity, with Ki values of 0.14-8.3 μM. Celiprolol has antihypertensive and antianginal activity, and can be used for the research of cardiovascular disease such as high blood pressure[1][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Beta-adrenergic receptor:0.14-8.3 μM (Ki) |
| In Vitro | Celiprolol (0-3 mM, 90 min) is uptaken by human small intestinal transporter OATP-A/1A2 in Xenopus Laevis oocytes[5]. Celiprolol (10 μM, 0-50 min) is transported across human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells by mediation of multiple transporters including P-glycoprotein[6]. |
| In Vivo | Celiprolol (Oral administration, 100 mg/kg/day for 31 days) improves endothelial function in the arteries of in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats, and restores it 4 weeks after endothelial denudation in the arteries of OLETF rats[2]. Celiprolol (Treated in drinking water, 10 mg/kg/day for 5 weeks) suppresses VCAM-1 expression by inhibition of oxidative stress, NF-κB, signal transduction, and increases eNOS via stimulation of the PI3K-Akt pathway, and improves cardiovascular remodeling in deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)-salt hypertensive rats[3]. Animal Model: Type II male Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) diabetic rats[2] Dosage: 100 mg/kg/day for 31 days Administration: Oral administration Result: Improved acetylcholine-induced NO-dependent relaxation in arteries. Improved tone-related basal NO release and acetylcholine-induced NO-dependent relaxation in the arteries and plasma NOx. Animal Model: Deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)-salt hypertensive rats [3] Dosage: 10 mg/kg/d for 5 weeks Administration: Treated in drinking water Result: Activated phosphorylation of eNOS through the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Modulated VCAM-1 expression, which is associated with inhibition of NF-κB phosphorylation. Reduced production of ROS by suppressing NAD(P)H oxidase subunit p22phox, p47phox, gp91phox, and nox1 expression. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 586.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H33N3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 379.494 |
| Flash Point | 308.5±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 379.247101 |
| PSA | 90.90000 |
| LogP | 1.92 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.545 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| 3-(3-Acetyl-4-{2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methyl-2-propanyl)amino]propoxy}phenyl)-1,1-diethylurea |
| 3-{3-Acetyl-4-[3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy]phenyl}-1,1-diethylurea |
| CCRIS 3400 |
| Celectol |
| 3-<3-Acetyl-4-(3-tert-butylamino-2-hydroxy-propoxy)-phenyl>-1,1-diethylharnstoff |
| EINECS 260-497-7 |
| Celiprololum [INN-Latin] |
| N-[3-acetyl-4-(3'-tert-butylamino-2'-hydroxy)propoxy]-phenyl-N'-diethylurea |
| Urea, N'-(3-acetyl-4-(3-((1,1-dimethylethyl)amino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)phenyl)-N,N-diethyl- |
| RHC-5320A |
| Urea, N'-[3-acetyl-4-[3-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-2-hydroxypropoxy]phenyl]-N,N-diethyl- |
| UL/1677 |
| N-[3-Acetyl-4-(3'-tert-butylamino-2'-hydroxy)propoxy]phenyl-N'-diethylurea |
| celiprolol |
| UNII:DRB57K47QC |
| N'-[3-Acetyl-4-[3-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-2-hydroxypropoxy]phenyl]-N,N-diethylurea |
| N'-(3-acetyl-4-(3-((1,1-dimethylethyl)-amino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-phenyl)-N,N-diethylurea |
| MFCD00864577 |
| [14C]-Celiprolol |
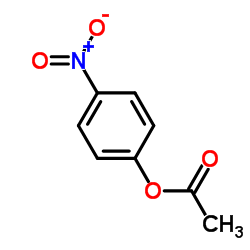 CAS#:830-03-5
CAS#:830-03-5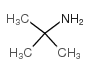 CAS#:75-64-9
CAS#:75-64-9![3-[3-ACETYL-4-(3-BROMO-2-HYDROXYPROPOXY)PHENYL]-1,1-DIETHYLUREA Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/194/85045-98-3.png) CAS#:85045-98-3
CAS#:85045-98-3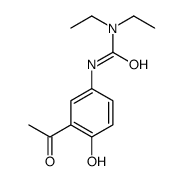 CAS#:79881-89-3
CAS#:79881-89-3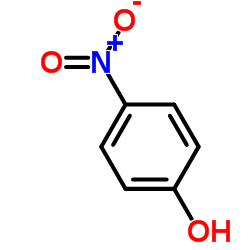 CAS#:100-02-7
CAS#:100-02-7 CAS#:1450-76-6
CAS#:1450-76-6 CAS#:329722-31-8
CAS#:329722-31-8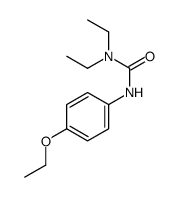 CAS#:1461-82-1
CAS#:1461-82-1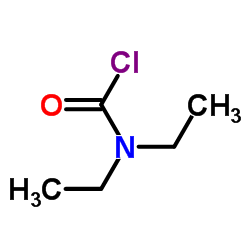 CAS#:88-10-8
CAS#:88-10-8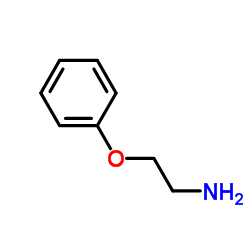 CAS#:156-43-4
CAS#:156-43-4 CAS#:57470-78-7
CAS#:57470-78-7