Ionomycin
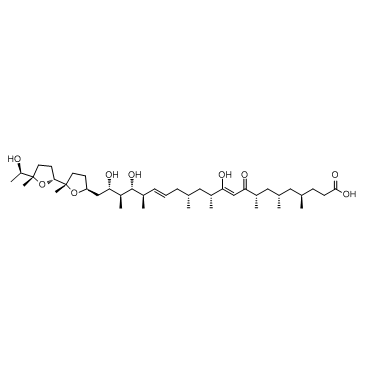
Ionomycin structure
|
Common Name | Ionomycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56092-81-0 | Molecular Weight | 709.00500 | |
| Density | 1.072 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 817.2ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C41H72O9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 235.2ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of IonomycinIonomycin is a Calcium ionophore and an antibiotic produced by Streptomyces conglobatus ATCC 31005. |
| Name | ionomycin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ionomycin is a Calcium ionophore and an antibiotic produced by Streptomyces conglobatus ATCC 31005. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Calcium channel[1]. |
| In Vitro | Ionomycin is a Calcium ionophore and an antibiotic produced by Streptomyces conglobatus ATCC 31005[1]. It is observed that LCLC 103H cells overexpressing the catalytic subunit of μ-calpain rapidly underwent cell death after treatment with ionomycin. The first signs of Ionomycin-induced cell death are detected 3 h after addition of the ionophore. Addition of 2 μM Ionomycin to LCLC 103H cells causes an instantaneous increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration from 50 to 180 nM. Remarkably, calcium concentrations are raised transiently to 0.8-1.5 μM. DNA and protein analysis in Ionomycin-treated cultures revealed DNA fragmentation and PARP cleavage to an 85-kDa fragment typical of caspase-mediated apoptosis. Three hours after addition of ionomycin, the percentage of early apoptotic cells approximately doubles. Necrosis could be detected in ~1-5% of the Ionomycin treated cells as supported by simultaneously positive fluorescein labeling and propidium iodide uptake. Caspase activation in whole cells was followed by monitoring the increase in activity against Ac-DEVD-amc following Ionomycin treatment[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.072 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 817.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C41H72O9 |
| Molecular Weight | 709.00500 |
| Flash Point | 235.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 708.51800 |
| PSA | 153.75000 |
| LogP | 7.79960 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.512 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | Soluble to 10 mM in Ethanol and to 10 mM in DMSO. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | 36-36/37/39-27-26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | NO0650000 |
| HS Code | 2941500000 |
| HS Code | 2941500000 |
|---|
|
Ca²⁺ signals promote GLUT4 exocytosis and reduce its endocytosis in muscle cells.
Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 307(2) , E209-24, (2014) Elevating cytosolic Ca(2+) stimulates glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, but how Ca(2+) affects intracellular traffic of GLUT4 is unknown. In tissue, changes in Ca(2+) leading to contraction preclude ... |
|
|
Regulation of T cell priming by lymphoid stroma.
PLoS ONE 6(11) , e26138, (2011) The priming of immune T cells by their interaction with dendritic cells (DCs) in lymph nodes (LN), one of the early events in productive adaptive immune responses, occurs on a scaffold of lymphoid str... |
|
|
Identification and characterization of IL-10/IFN-gamma-producing effector-like T cells with regulatory function in human blood.
J. Exp. Med. 206(5) , 1009-17, (2009) Two subsets of natural and adaptive regulatory T (T reg) cells have been described, but the identity of adaptive type 1 regulatory (Tr1)-like cells in humans is unclear. We analyzed a subset of human ... |
| 10,16-Docosadienoic acid, 11,19,21-trihydroxy-4,6,8,12,14,18,20-heptamethyl-22-[(2S,2'R,5S,5'S)-octahydro-5'-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2,5'-dimethyl[2,2'-bifuran]-5-yl]-9-oxo-, (4R,6S,8S,10Z,12R,14R,16E,18R,19R,20S,21S)- |
| (4R,6S,8S,10Z,12R,14R,16E,18R,19R,20S,21S)-11,19,21-Trihydroxy-22-{(2S,2'R,5S,5'S)-5'-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2,5'-dimethyloctahydro-2,2'-bifuran-5-yl}-4,6,8,12,14,18,20-heptamethyl-9-oxo-10,16-docosadienoic acid |
| Ionomycin |
| Ionomycin free acid,(4R,6S,8S,10Z,12R,14R,16E,18R,19R,20S,21S)-11,19,21-Trihydroxy-4,6,8,12,14,18,20-heptamethyl-22-[(2S,2'R,5S,5'S)-octahydro-5'-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2,5'-dimethyl[2,2'-bifuran]-5-yl]-9-oxo-10,16-docosadienoicacid |
| Ionomycin,Free Acid,from Streptomyces conglbatus |
| MFCD00036890 |
| Ionomycinefreeacid |
| Ionomycin from Streptomyces conglobatus |
| IONOMYCIN,STREPTOMYCES CONGLOBATUS |
| (4R,6S,8S,10Z,12R,14R,16E,18R,19R,20S,21S)-11,19,21-Trihydroxy-22-{(2S,2'R,5S,5'S)-5'-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-2,5'-dimethyloctahydro-2,2'-bifuran-5-yl}-4,6,8,12,14,18,20-heptamethyl-9-oxodocosa-10,16-dienoic acid |
| Ionomycin free acid |
| Ionomycin,Free Acid,Streptomyces conglobatus |
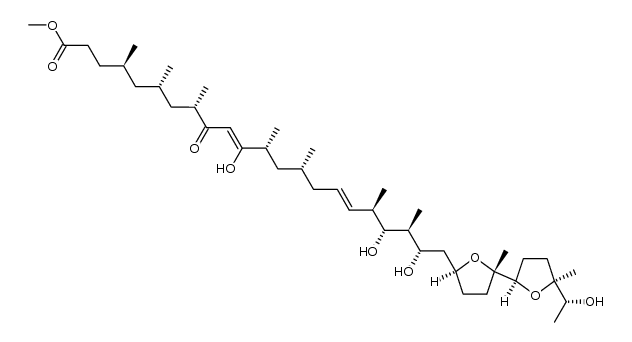 CAS#:110497-18-2
CAS#:110497-18-2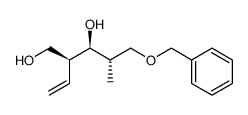 CAS#:73814-77-4
CAS#:73814-77-4![(1S,2R,6R,4Z)-5-(3'-(benzyloxy)propyl)-1,2,4-trimethyl-3,9-dioxabicyclo[4.2.1]non-4-ene Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/162/128329-77-1.png) CAS#:128329-77-1
CAS#:128329-77-1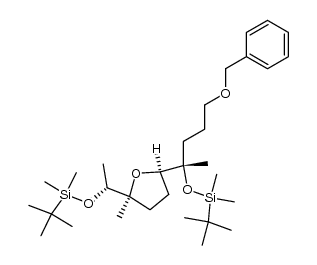 CAS#:128329-80-6
CAS#:128329-80-6
