Coumaphos
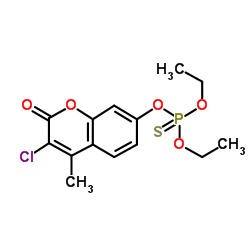
Coumaphos structure
|
Common Name | Coumaphos | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56-72-4 | Molecular Weight | 362.766 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 449.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H16ClO5PS | Melting Point | 91ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 225.9±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of CoumaphosCoumaphos is aorganothiophosphorus cholinesterase inhibitor that is used as an anthelmintic, insecticide, and as a nematocide. |
| Name | coumaphos |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 449.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 91ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C14H16ClO5PS |
| Molecular Weight | 362.766 |
| Flash Point | 225.9±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 362.014465 |
| PSA | 99.80000 |
| LogP | 3.86 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.578 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with alkalies, strong oxidising agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300-H312-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P273-P280-P301 + P310-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T+: Very toxic;N: Dangerous for the environment; |
| Risk Phrases | R21;R28;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S28-S36/37-S45-S60-S61-S36-S26-S16 |
| RIDADR | 2783 |
| RTECS | GN6300000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
|
~58% 
Coumaphos CAS#:56-72-4 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 49, # 1 p. 246 - 255 |
|
Genomic analysis of the interaction between pesticide exposure and nutrition in honey bees (Apis mellifera).
J. Insect Physiol. 71 , 177-90, (2014) Populations of pollinators are in decline worldwide. These declines are best documented in honey bees and are due to a combination of stressors. In particular, pesticides have been linked to decreased... |
|
|
Photodegradation of organophosphorus pesticides in honey medium.
Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 108 , 84-8, (2014) Honey can be polluted due to environmental pollution and misuse of beekeeping practices. In the present study, photodegradation experiments of organophosphorus pesticides (coumaphos, methyl parathion ... |
|
|
Honey constituents up-regulate detoxification and immunity genes in the western honey bee Apis mellifera.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110(22) , 8842-6, (2013) As a managed pollinator, the honey bee Apis mellifera is critical to the American agricultural enterprise. Recent colony losses have thus raised concerns; possible explanations for bee decline include... |
| Agridip |
| Coumaphos |
| Meldone |
| Baymix |
| Phosphorothioic acid, O- (3-chloro-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-7-yl) O,O-diethyl ester |
| 3-chloro-7-diethoxyphosphinothioyloxy-4-methylcoumarin |
| Asuntol |
| 3-Chlor-7-diaethoxythiophosphoryloxy-4-methyl-cumarin |
| Meldane |
| Azunthol |
| Phosphorothioic acid, O-(3-chloro-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-7-yl) O,O-diethyl ester |
| 3-chloro-7-diethoxythiophosphoryloxy-4-methyl-coumarin |
| EINECS 200-285-3 |
| Coumaphos [BAN] |
| O-(3-Chlor-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl)-O,O-diethylthiophosphat |
| O-(3-chloro-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-7-yl) O,O-diethyl phosphorothioate |
| Muscatox |
| Thiophosphate de O-(3-chloro-4-méthyl-2-oxo-2H-chromén-7-yle) et de O,O-diéthyle |
| O-(3-chloro-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl) O,O-diethylphosphorothioate |
| 3-chloro-7-diethoxyphosphinothioyloxy-4-methylchromen-2-one |
| O-3-chloro-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl O,O-diethyl phosphorothioate |
| O-(3-Chloro-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl) O,O-diethyl phosphorothioate |
| Asunthol |
| Coumafos |
| MFCD00041820 |
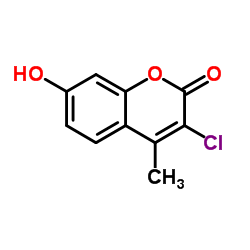
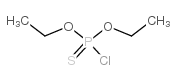
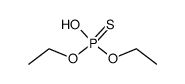 CAS#:2465-65-8
CAS#:2465-65-8