L-NMMA acetate
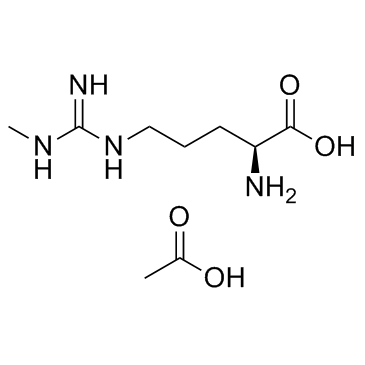
L-NMMA acetate structure
|
Common Name | L-NMMA acetate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 53308-83-1 | Molecular Weight | 248.279 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 392.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H20N4O4 | Melting Point | 180-190ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 191.3ºC | |
Use of L-NMMA acetateL-NMMA acetate is a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor of all NOS isoforms including NOS1, NOS2, and NOS3. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse) are approximately 0.18, 0.4, and 6 µM, respectively. |
| Name | ng-monomethyl-l-arginine acetate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-NMMA acetate is a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor of all NOS isoforms including NOS1, NOS2, and NOS3. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse) are approximately 0.18, 0.4, and 6 µM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 0.18 µM (nNOS), 0.4 µM (eNOS), 6 µM (iNOS)[1] |
| In Vitro | L-NMMA, starting from 100 μM, produces a concentration-dependent inhibition of the evoked relaxations (2Hz); maximal inhibition at 1 mM averaged about 35%. The inhibitory effect of L-NMMA is unchanged by previous incubation with D-arginine while it is prevented by L-arginine (L-Arg). L-NMMA does not affect isoprenaline-induced relaxation[2]. Superfusion of L-NMMA reduces arteriolar diameter and causes dose-dependent increases in arteriolar tone. The onset of action of L-NMMA is nearly immediate. L-NMMA inhibits vasodilator responses to the endothelium-dependent vasodilator ACh but not to the endothelium-independent NP. NE induced dose-related vasoconstriction that is significantly potentiated by L-NMMA[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | NOS activity is determined by monitoring the conversion of L-[14C]arginine to [14C]citrulline. For nNOS, reaction mixtures contain, in a final volume of 200 μL, 20 mM Na+ HEPES buffer, pH 7.5, 100 μM EDTA, 2 mM CaCl2, 10 μg/mL calmodulin, 500 μM dithiothreitol, 100 μM THB, 25 μM FAD, 25 μM FMN, 100 μg/mL bovine serum albumin, 20 μM L-[14C]citrulline, 500 PM NADPH, and enzyme. Reaction is initiated by the addition of L-[14C]citrulline; reaction temperature is 25°C. At appropriate times, typically 3.5, 7, and 10.5 min, 50-1.11 portions are removed and added to 200 pl of a stopping solution of 100 mM Na+ HEPES buffer, pH 5.5, containing 5 mM EGTA. Those samples are immediately heated for 1 min in a boiling water bath, chilled, and centrifuged. A portion (225 μL) of the supernatant is fractionated on small Dowex 50 columns. [14C]citrulline is eluted with 2 ml of water and is quantitated by liquid scintillation counting[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 392.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 180-190ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C9H20N4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 248.279 |
| Flash Point | 191.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 248.148453 |
| PSA | 148.53000 |
| LogP | 0.59500 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29252900 |
|
Evidence of oxidative stress and mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction in an in vitro model of sepsis-induced kidney injury.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1837(10) , 1790-800, (2014) To investigate the role of oxidative stress and/or mitochondrial impairment in the occurrence of acute kidney injury (AKI) during sepsis, we developed a sepsis-induced in vitro model using proximal tu... |
|
|
PRMT9 is a type II methyltransferase that methylates the splicing factor SAP145.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6428, (2015) The human genome encodes a family of nine protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMT1-9), whose members can catalyse three distinct types of methylation on arginine residues. Here we identify two splic... |
|
|
Heparin modulation on hepatic nitric oxide synthase in experimental steatohepatitis.
Exp. Ther. Med. 8(5) , 1551-1558, (2014) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is considered to be a hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome, and has been etiologically associated with insulin resistance (IR). The histopathology of NA... |
| L-NMMA MONOACETATE |
| ANO 1020 |
| NG-Methyl-L-arginine acetate salt |
| H-ARG(ME)-OH ACOH |
| NG-Monomethyl-L-arginine monoacetate |
| NMMA ACETATE SALT |
| Nω-Monomethyl-L-arginine Acetate |
| MFCD00069311 |
| L-NMMA,ACETATE SALT |
| NoMega-MonoMethyl-L-arginine Acetate |
| NG-ME-L-ARG,ACOH |
| NG-Methylarginine acetate |
| Nω-Methyl-L-arginine Acetate |
| L-NMMA ACETATE |
| NMMA |
| L-Ornithine, N-[imino(methylamino)methyl]-, acetate (1:1) |
| N-(N-Methylcarbamimidoyl)-L-ornithine acetate (1:1) |
| L-NMMA |
| Tilarginine acetate |

