Coproporphyrin I
Modify Date: 2025-08-24 17:36:41
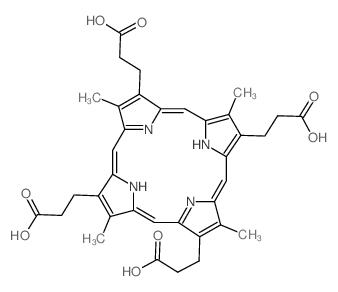
Coproporphyrin I structure
|
Common Name | Coproporphyrin I | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 531-14-6 | Molecular Weight | 654.70900 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C36H38N4O8 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Coproporphyrin ICoproporphyrin I is an endogenous metabolite present in Urine and Blood that can be used for the research of Liver Disease and Porphyria[1][2][3][4]. |
| Name | 3-[7,12,17-tris(2-carboxyethyl)-3,8,13,18-tetramethyl-21,22-dihydroporphyrin-2-yl]propanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Coproporphyrin I is an endogenous metabolite present in Urine and Blood that can be used for the research of Liver Disease and Porphyria[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Endogenous metabolites is defined as those that are annotated by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes as substrates or products of the ~1900 metabolic enzymes encoded in our genome. It is clear in the body of literature that there are documented toxic properties for many of these metabolites[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C36H38N4O8 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 654.70900 |
| Exact Mass | 654.26900 |
| PSA | 205.50000 |
| LogP | 3.09360 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.638 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| Coproporphyrin I |
| coproporphyrin-I tetracarboxylic acid |
| coproporphyrine I |
| coproporphyrin I-3,8,13,18-tetramethyl-21H,23H-porphine-2,7,12,17-tetrapropionic acid |
| 3,8,13,18-tetramethyl-21H,23H-porphyrin 2,7,12,17-tetrapropionic acid |
| 3,8,13,18-Tetramethyl-21H,23H-porphine-2,7,12,17-tetrapropionic acid |
 CAS#:872535-45-0
CAS#:872535-45-0 CAS#:10170-03-3
CAS#:10170-03-3 CAS#:132281-87-9
CAS#:132281-87-9![2-formyl-3-[2-(methoxycarbonyl)ethyl]-4-methylpyrrole Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/019/34463-53-1.png) CAS#:34463-53-1
CAS#:34463-53-1![[5-bromo-3-(2-carboxy-ethyl)-4-methyl-pyrrol-2-yl]-[4-(2-carboxy-ethyl)-3,5-dimethyl-pyrrol-2-ylidene]-methane, hydrobromide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/221/37531-58-1.png) CAS#:37531-58-1
CAS#:37531-58-1 CAS#:54278-10-3
CAS#:54278-10-3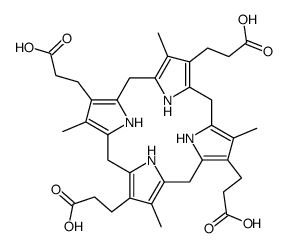 CAS#:31110-56-2
CAS#:31110-56-2 CAS#:37789-64-3
CAS#:37789-64-3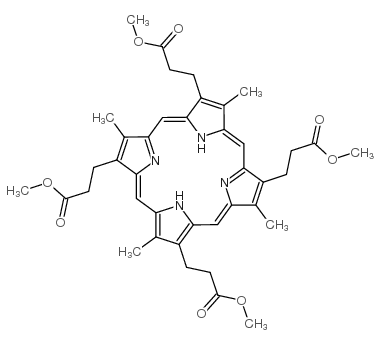 CAS#:25767-20-8
CAS#:25767-20-8