bis(8-hydroxyquinolinium) sulphate
Modify Date: 2025-09-11 09:49:45
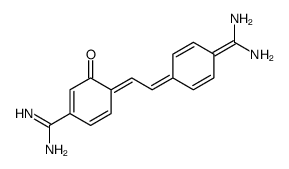
bis(8-hydroxyquinolinium) sulphate structure
|
Common Name | bis(8-hydroxyquinolinium) sulphate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 495-99-8 | Molecular Weight | 280.32400 | |
| Density | 1.288g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 509.678ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H16N4O | Melting Point | 235° | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 262.044ºC | |
Use of bis(8-hydroxyquinolinium) sulphateHydroxystilbamidine, a dye capable of binding to both DNA and RNA, has been found to be a powerful inhibitor of cellular ribonucleases. |
| Name | (4E)-4-[2-[4-(diaminomethylidene)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene]ethylidene]-3-oxocyclohexa-1,5-diene-1-carboximidamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Hydroxystilbamidine, a dye capable of binding to both DNA and RNA, has been found to be a powerful inhibitor of cellular ribonucleases. |
|---|---|
| In Vitro | Hydroxystilbamidine permits the recovery of mRNA after polysome released with Nonidet P-40 (NP-40). Sucrose gradient analysis of detergent-lysed postnuclear supernates is used to analyze the size distribution of NP-40-released polysomes. The heparin gradient shows some polyribosomes, whereas the Hydroxystilbamidine gradient shows a remarkably large peak of very heavy polyribosomes. This peak is obtained reproducibly if Hydroxystilbamidine is present before the addition of NP-40[1]. |
| In Vivo | Hydroxystilbamidine is an effective suppressor of the plaque-forming cell (PFC) response when given before sheep erythrocytes (SRBC) stimulation. Hydroxystilbamidine depresses the plaque response of the treated mice. Fewer PFC are observed in Hydroxystilbamidine-treated mice throughout the experiment, but the level of suppression decreases with time. By day 14, the number of PFC observed in both the Hydroxystilbamidine treated mice and the control group is essentially at the background level[2]. |
| References | 1. Lizardi PM. Isolation of giant silk fibroin polysomes and fibroin mRNP particles using a novel ribonuclease inhibitor, hydroxystilbamidine. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):292-6. |
| Density | 1.288g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 509.678ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 235° |
| Molecular Formula | C16H16N4O |
| Molecular Weight | 280.32400 |
| Flash Point | 262.044ºC |
| Exact Mass | 280.13200 |
| PSA | 118.98000 |
| LogP | 1.57850 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.654 |
| InChIKey | TUESWZZJYCLFNL-DAFODLJHSA-N |
| SMILES | N=C(N)c1ccc(C=Cc2ccc(C(=N)N)cc2O)cc1 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| 2-Hydroxy-4,4'-stilbenedicarboxamidine |
| EINECS 207-811-0 |
| Oxistilbamidinum |
| HYDROXYSTILBAMIDINE |
| 2-Hydroxy-4,4'-diguanylstilbene |