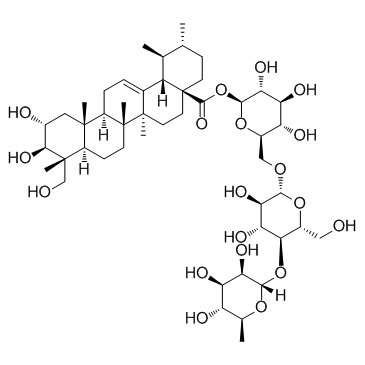
Asiatic acid

Asiatic acid structure
|
Common Name | Asiatic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 464-92-6 | Molecular Weight | 488.699 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 609.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H48O5 | Melting Point | 325-330 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 336.4±28.0 °C | |
Use of Asiatic acidAsiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene found in Centella asiatica, induces apoptosis in melanoma cells. Asiatic acid can be used to treat skin cancer[1]. Asiatic acid also has anti-inflammatory activities[2]. |
| Name | asiatic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Asiatic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene found in Centella asiatica, induces apoptosis in melanoma cells. Asiatic acid can be used to treat skin cancer[1]. Asiatic acid also has anti-inflammatory activities[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 609.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 325-330 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C30H48O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 488.699 |
| Flash Point | 336.4±28.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 488.350189 |
| PSA | 97.99000 |
| LogP | 6.46 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±4.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.579 |
| InChIKey | JXSVIVRDWWRQRT-UYDOISQJSA-N |
| SMILES | CC1CCC2(C(=O)O)CCC3(C)C(=CCC4C5(C)CC(O)C(O)C(C)(CO)C5CCC43C)C2C1C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2918199090 |
|
~% 
Asiatic acid CAS#:464-92-6 |
| Literature: SHANGHAI INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY (SIPI) Patent: WO2009/89365 A2, 2009 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 6-7 ; |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2918199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2918199090 other carboxylic acids with alcohol function but without other oxygen function, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Biopharmaceutical and pharmacokinetic characterization of asiatic acid in Centella asiatica as determined by a sensitive and robust HPLC-MS method.
J. Ethnopharmacol. 163 , 31-8, (2015) Asiatic acid is one of the main components in the herb Centella asiatica, which is a well-known herbal medicine for its excellent pharmacological effects. To enhance the development potentials of asia... |
|
|
Asiatic acid ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine experimental colitis via suppressing mitochondria-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Int. Immunopharmacol. 24(2) , 232-8, (2015) In the present study, the effect of asiatic acid, a natural triterpenoid compound, on murine experimental colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) and its possible mechanism were examined in vi... |
|
|
Effecting skin renewal: a multifaceted approach.
J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 10(2) , 126-30, (2011) The skin undergoes intrinsic aging as a normal course, but exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light results in major cumulative damage that manifests as the typical aged photodamaged skin. UV irradiation pr... |
| 2,3,23-TRIHYDROXY-12-URSEN-28-OIC ACID |
| (2α,3β)-2,3,23-Trihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid |
| Asiatic acid |
| Urs-12-en-28-oic acid, 2,3,23-trihydroxy-, (2α,3β)- |
| Asiantic acid |
| Asiaticacid |
| UNII-9PA5A687X5 |
| MFCD00238541 |
| Dammarolic acid |
| EINECS 482-720-9 |