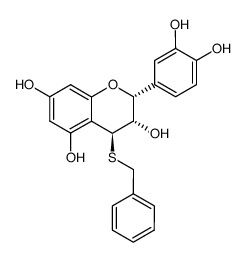
Procyanidin C1
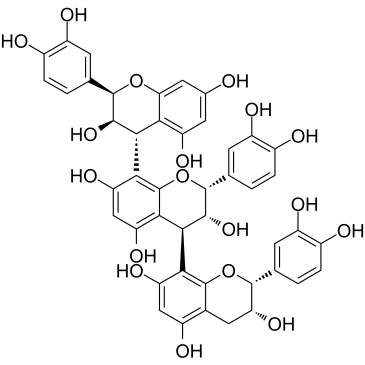
Procyanidin C1 structure
|
Common Name | Procyanidin C1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 37064-30-5 | Molecular Weight | 866.77200 | |
| Density | 1.747g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C45H38O18 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Procyanidin C1Procyanidin C1 is a natural polyphenol, causes DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, and induces apoptosis. Procyanidin C1 decreases the level of Bcl-2, but enhances BAX, caspase 3 and 9 expression in cancer cells[1]. |
| Name | procyanidin C1 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Procyanidin C1 is a natural polyphenol, causes DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, and induces apoptosis. Procyanidin C1 decreases the level of Bcl-2, but enhances BAX, caspase 3 and 9 expression in cancer cells[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Apoptosis[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.747g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C45H38O18 |
| Molecular Weight | 866.77200 |
| Exact Mass | 866.20600 |
| PSA | 331.14000 |
| LogP | 4.44390 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.826 |
| Storage condition | ?20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
~98% 
Procyanidin C1 CAS#:37064-30-5 |
| Literature: Kozikowski, Alan P.; Tuckmantel, Werner; Romanczyk JR., Leo J. Patent: US2004/116718 A1, 2004 ; Location in patent: Page 10 ; |
|
~% 
Procyanidin C1 CAS#:37064-30-5 |
| Literature: Morimoto; Nonaka; Nishioka Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1986 , vol. 34, # 2 p. 633 - 642 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Morimoto; Nonaka; Nishioka Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1986 , vol. 34, # 2 p. 633 - 642 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Morimoto; Nonaka; Nishioka Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1986 , vol. 34, # 2 p. 633 - 642 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Morimoto; Nonaka; Nishioka Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1986 , vol. 34, # 2 p. 633 - 642 |
|
UHPLC-PDA-ESI/HRMSn profiling method to identify and quantify oligomeric proanthocyanidins in plant products.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(39) , 9387-400, (2014) Oligomeric proanthocyanidins were successfully identified by UHPLC-PDA-HRMS(n) in a selection of plant-derived materials (jujube fruit, Fuji apple, fruit pericarps of litchi and mangosteen, dark choco... |
|
|
A galloylated dimeric proanthocyanidin from grape seed exhibits dentin biomodification potential.
Fitoterapia 101 , 169-78, (2015) Grape seeds are a rich source of polyphenols, especially proanthocyanidins (PACs), and are also known for the presence of galloylated oligomeric PACs (OPACs). The present study focuses on the phytoche... |
| Procyanidol C1 |
| (2R,3R,4S)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-4-[(2R,3R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-8-yl]-8-[(2R,3R,4R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-4-yl]-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,5,7-triol |
| Procyanidin C1 |


![[epicatechin-(4β→8)]5-epicatechin structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/196/88847-05-6.png)
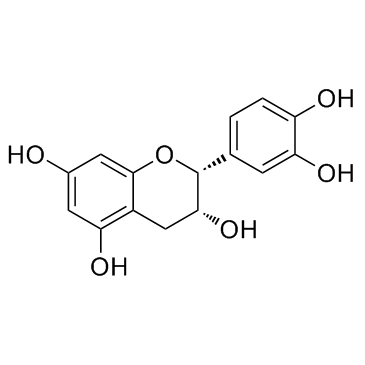 CAS#:490-46-0
CAS#:490-46-0
