Ganglioside GM2 Asialo Mixture
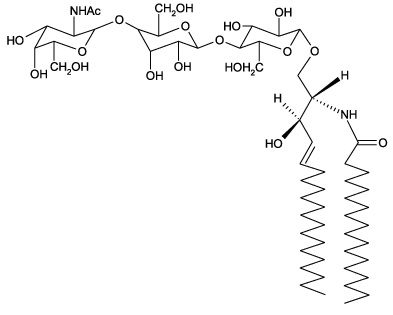
Ganglioside GM2 Asialo Mixture structure
|
Common Name | Ganglioside GM2 Asialo Mixture | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 35960-33-9 | Molecular Weight | 1093.4 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C56H104N2O18 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Ganglioside GM2 Asialo MixtureGanglioside GM2 asialo (asialo-GM2) is a glycosphingolipid containing three monosaccharide residues and one fatty acid of variable chain length, but lacks the sialic acid residue present on ganglioside M2. Asialo-GM2 is found at low or undetectable levels in normal human brains, but it accumulates in the brains of patients with Tay-Sachs disease and Sandhoff disease, which are expressed as lysosomal β- A neurodegenerative disorder characterized by hexosaminidase A and B deficiency. It also binds to various bacteria, including Pseudomonas isolated from cystic fibrosis patients. The Asialo-GM2 mixture contains ganglioside GM2 asialo molecular species with fatty acyl chains of variable length. |
| Name | Asialoganglioside GM<sub>2</sub> |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ganglioside GM2 asialo (asialo-GM2) is a glycosphingolipid containing three monosaccharide residues and one fatty acid of variable chain length, but lacks the sialic acid residue present on ganglioside M2. Asialo-GM2 is found at low or undetectable levels in normal human brains, but it accumulates in the brains of patients with Tay-Sachs disease and Sandhoff disease, which are expressed as lysosomal β- A neurodegenerative disorder characterized by hexosaminidase A and B deficiency. It also binds to various bacteria, including Pseudomonas isolated from cystic fibrosis patients. The Asialo-GM2 mixture contains ganglioside GM2 asialo molecular species with fatty acyl chains of variable length. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Molecular Formula | C56H104N2O18 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1093.4 |
| InChIKey | FOCMISOLVPZNSV-CYSIEEFGSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCCC=CC(O)C(COC1OC(CO)C(OC2OC(CO)C(OC3OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C3NC(C)=O)C(O)C2O)C(O)C1O)NC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Asialo GM-2 developed on the fatty streak of atherosclerotic aorta detected by a novel monoclonal antibody (ASH1a/256C).
Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 748 , 277-81; discussion 281-2, (1995)
|
|
|
Catabolism of asialo-GM2 in man and mouse. Specificity of human/mouse chimeric GM2 activator proteins.
J. Biol. Chem. 274(40) , 28612-8, (1999) Tay-Sachs disease is an inborn lysosomal disease characterized by excessive cerebral accumulation of GM2. The catabolism of GM2 to GM3 in man requires beta-hexosaminidase A (HexA) and a protein cofact... |
|
|
Optimal conditions to radiolabel (3H or 14C) aminosugar-containing glycosphingolipids by de-N-acetylation and re-N-acetylation.
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1244(2-3) , 418-22, (1995) The optimal conditions were examined for selective re-N-acetylation with 14C or 3H.acetic anhydride of de-N-acetylated aminosugar-containing glycosphingolipids. Re-N-acetylation, which is nearly quant... |
| MFCD00131129 |