Axitinib
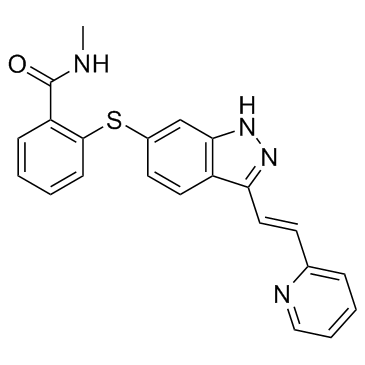
Axitinib structure
|
Common Name | Axitinib | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 319460-85-0 | Molecular Weight | 386.470 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 668.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H18N4OS | Melting Point | 213-215ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 358.3±31.5 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of AxitinibAxitinib is a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor with IC50s of 0.1, 0.2, 0.1-0.3, 1.6 nM for VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3 and PDGFRβ, respectively. |
| Name | axitinib |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Axitinib is a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor with IC50s of 0.1, 0.2, 0.1-0.3, 1.6 nM for VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3 and PDGFRβ, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
VEGFR1:0.1 nM (IC50) VEGFR2:0.2 nM (IC50) VEGFR3:0.1 nM (IC50) PDGFRβ:1.6 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Axitinib (AG-013736) is a potent and selective inhibitor of VEGFR 1 to 3. In transfected or endogenous RTK-expressing cells, Axitinib potently blocks growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 with average IC50 values of 0.2 and 0.1 to 0.3 nM, respectively. Cellular activity against VEGFR-1 is 1.2 nM (measured in the presence of 2.3% bovine serum albumin), equivalent to an absolute IC50 of ~0.1 nM, based on protein binding of Axitinib. The potency against murine VEGFR-2 (Flk-1) in Flk-1-transfected NIH-3T3 cells is 0.18 nM, similar to that of its human homologue. Axitinib shows ~8- to 25-fold higher IC50 against the closely related type III and V family RTKs, including PDGFR-β (1.6 nM), KIT (1.7 nM), and PDGFR-α (5 nM); nanomolar concentrations of Axitinib blocks PDGF BB-mediated human glioma U87MG cell (PDGFR-β-positive) migration but not proliferation[2]. |
| In Vivo | A single oral dose of Axitinib (100 mg/kg) markedly suppresses murine VEGFR-2 phosphorylation for up to 7 h compared with control tumors. Axitinib rapidly inhibits VEGF-induced vascular permeability in the skin of mice; the inhibition is dose-dependent and directly correlated with drug concentration in mice. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis indicate an unbound EC50 of 0.46 nM. Similar inhibitory effects are also shown in the skin of MV522 tumor-bearing mice without exogenous VEGF-A stimulation. Axitinib inhibits the growth of human xenograft tumors in mice. Axitinib produces dose-dependent growth delay regardless of initial tumor size, model type, or implant site[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Endothelial or tumor cells are starved for 18 h in the presence of either 1% FBS (HUVEC) or 0.1% FBS (tumor cells). Axitinib is added and cells are incubated for 45 min at 37°C in the presence of 1 mM Na3VO4. The appropriate growth factor is added to the cells, and after 5 min, cells are rinsed with cold PBS and lysed in the lysis buffer and a protease inhibitor cocktail. The lysates are incubated with immunoprecipitation antibodies for the intended proteins overnight at 4°C. Antibody complexes are conjugated to protein A beads and supernatants are separated by SDS-PAGE[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice and Rats[2] Mice with M24met xenograft tumors (400-600 mm3) are administered with a single dose of Axitinib or the control (0.5% carboxymethylcellulose/H2O). Blood and tumor tissue samples are collected for pharmacokinetic and VEGFR-2 measurements. Total protein concentrations in tumor tissues are determined using the Bradford colorimetric assay. Six-day-old Sprague-Dawley rats are given two i.p. injections of Axitinib (30 mg/kg ). Animals are sacrificed, retinas are collected and lysed, and immunoprecipitation/immunoblotting experiments are done. ECL-Plus is used for detection and densitometry analysis is done using the Alpha Imager 8800. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 668.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 213-215ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C22H18N4OS |
| Molecular Weight | 386.470 |
| Flash Point | 358.3±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 386.120117 |
| PSA | 95.97000 |
| LogP | 4.15 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.728 |
| InChIKey | RITAVMQDGBJQJZ-FMIVXFBMSA-N |
| SMILES | CNC(=O)c1ccccc1Sc1ccc2c(C=Cc3ccccn3)n[nH]c2c1 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Heparan sulfate D-glucosaminyl 3-O-sulfotransferase-3B1 (HS3ST3B1) promotes angiogenesis and proliferation by induction of VEGF in acute myeloid leukemia cells.
J. Cell. Biochem. 116(6) , 1101-12, (2015) Heparan sulfate (HS) are complex polysaccharides that reside on the plasma membrane of almost all mammalian cells, and play an important role in physiological and pathological conditions. Heparan sulf... |
|
|
Involvement of corneal lymphangiogenesis in a mouse model of allergic eye disease.
Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 56 , 3140-8, (2015) The contribution of lymphangiogenesis (LA) to allergy has received considerable attention and therapeutic inhibition of this process via targeting VEGF has been considered. Likewise, certain inflammat... |
|
|
Chronic inflammation, lymphangiogenesis, and effect of an anti-VEGFR therapy in a mouse model and in human patients with aspiration pneumonia.
J. Pathol. 235(4) , 632-45, (2015) Chronic inflammation induces lymphangiogenesis and blood vessel remodelling. Since aged pneumonia patients often have repeated episodes of aspiration pneumonia, the pathogenesis may involve chronic in... |
| N-Methyl-2-({3-[(E)-2-(2-pyridinyl)vinyl]-1H-indazol-6-yl}sulfanyl)benzamide |
| Benzamide, N-methyl-2-[[3-[(E)-2-(2-pyridinyl)ethenyl]-1H-indazol-6-yl]thio]- |
| UNII-C9LVQ0YUXG |
| Inlyta |
| Benzamide, N-methyl-2-[[3-[(1E)-2-(2-pyridinyl)ethenyl]-1H-indazol-6-yl]thio]- |
| 10mg |
| Axitinib (usan) |
| N-Methyl-2-({3-[(E)-2-(pyridin-2-yl)vinyl]-1H-indazol-6-yl}sulfanyl)benzamide |
| AG-013736 N-Methyl-2-((3-((1E)-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethenyl)-1H-indazol-6-yl)sulfanyl)benzamide |
| Axtinib |
| AVERMECTINB |
| Axitinib |
| N-methyl-2-({3-[(E)-2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethenyl]-1H-indazol-6-yl}sulfanyl)benzamide |
| [14C]-Axitinib |
 CAS#:100-69-6
CAS#:100-69-6 CAS#:885126-34-1
CAS#:885126-34-1