TSU-68 (SU6668, Orantinib)
Modify Date: 2025-08-22 07:29:14
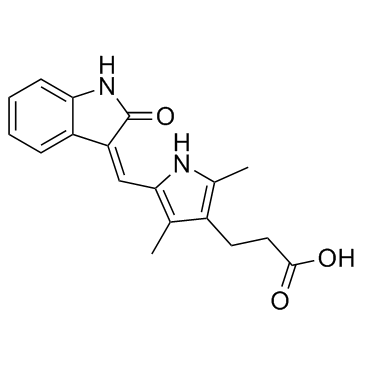
TSU-68 (SU6668, Orantinib) structure
|
Common Name | TSU-68 (SU6668, Orantinib) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 252916-29-3 | Molecular Weight | 310.347 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 590.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H18N2O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 310.9±30.1 °C | |
Use of TSU-68 (SU6668, Orantinib)Orantinib (SU6668; TSU-68) is a multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with Kis of 2.1 μM, 8 nM and 1.2 μM for Flt-1, PDGFRβ and FGFR1, respectively. |
| Name | 3-{2,4-dimethyl-5-[(2-oxo(1H-benzo[d]azolidin-3-ylidene))-methyl]pyrrol-3-yl}propanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Orantinib (SU6668; TSU-68) is a multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with Kis of 2.1 μM, 8 nM and 1.2 μM for Flt-1, PDGFRβ and FGFR1, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Flt-1:2.1 μM (Ki) PDGFRβ:0.008 μM (Ki) FGFR1:1.2 μM (Ki) |
| In Vitro | Orantinib (SU6668; 0.03-10 μM) shows inhibitory activity against tyrosine phosphorylation of KDR in VEGF stimulated HUVECs, and also blocks PDGF-stimulated PDGFRβ tyrosine phosphorylation in NIH-3T3 cells overexpressing PDGFRβ. Orantinib (≥10 μM) inhibits acidic FGF-induced phosphorylation of the FGFR1 substrate 2. However, Orantinib (up to 100 μM) has no effect on EGF-stimulated EGFR tyrosine phosphorylation in NIH-3T3 cells overexpressing EGFR. Furthermore, Orantinib inhibits VEGF-driven and FGF-driven mitogenesis of HUVECs with mean IC50 of 0.34 μM and 9.6 μM, respectively[1]. In human myeloid leukemia MO7E cells, Orantinib (SU6668) inhibits the tyrosine autophosphorylation of stem cell factor (SCF) receptor, c-kit, with IC50 of 0.1-1 μM, as well as ERK1/2 phosphorylation. In addition, Orantinib suppresses SCF-induced proliferation of MO7E cells with an IC50 of 0.29 μM, and induces apoptosis[2]. |
| In Vivo | Orantinib (SU6668; 75-200 mg/kg) causes tumor growth inhibition on several tumor types in xenograft models in athymic mice, such as A375, Colo205, H460, Calu-6, C6, SF763T, and SKOV3TP5 cells. Orantinib (75 mg/kg) also inhibits tumor angiogenesis of C6 glioma xenografts[1]. In a tumor model of HT29 human colon carcinoma, Orantinib (200 mg/kg) decreases the average vessel permeability and average fractional plasma volume in the tumor rim and core. Orantinib enhances abnormal stromal development at the periphery of carcinomas[3]. Moreover, Orantinib (TSU-68; 200 mg/kg) augments the effect of chemotherapeutic infusion in a rabbit VX2 liver tumor model[4]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are seeded (3×105 cells/35-mm well) in DMEM containing 10% (v/v) FBS and grow to confluence and then quiesced in DMEM containing 0.1% serum for 2 hours before drug treatment. HUVECs (seeded at 2×106 cells/10-cm plate) are grown to confluence in endothelial cell growth media and then quiesced in endothelial cell basal media containing 0.5% FBS for 24 hours before drug treatment. All cell lines are incubated with Orantinib for 1 hour before ligand stimulation (100 ng/mL) for 10 min. |
| Animal Admin | Colo205 and H460 cells are cultured in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FBS and 2 mm glutamine. SKOV3 cells are passaged five times through mice to yield SKOV3TP5 cells. These cells are cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and 2 mm glutamine. Tumor cells (3-10×106 cells/animal) are implanted s.c. into the hind flank of mice on day 0. Daily treatment with Orantinib or vehicle commenced 1 day after implantation of cells (to test efficacy against newly implanted tumors) or when tumors have reached a predetermined average size (to test efficacy against established tumors). Orantinib is delivered i.p. by bolus injection in DMSO or p.o. by gavage in a cremophor-based vehicle according to the specifics stated in figure and table legends. Tumor growth is measured twice a week using vernier calipers for the duration of treatment. Tumor volumes are calculated. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 590.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H18N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 310.347 |
| Flash Point | 310.9±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 310.131744 |
| PSA | 82.19000 |
| LogP | 2.49 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.675 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| TSU-68,SU6668,Orantinib) |
| 3-(2,4-Dimethyl-5-(2-oxo-1,2-dihydroindol-3-ylidenemethyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)propionic acid |
| TSU-68 |
| 1H-Pyrrole-3-propanoic acid, 5-((1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl)-2,4-dimethyl- |
| 3-{2,4-Dimethyl-5-[(Z)-(2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-1H-pyrrol-3-yl}propanoic acid |
| 3-(2,4-Dimethyl-5-((2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)propionic acid |
| Orantinib |
| 1H-Pyrrole-3-propanoic acid, 5-[(Z)-(1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-2,4-dimethyl- |
| 5-((1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl)-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-propanoic acid |