Lansoprazole (sodium)
Modify Date: 2025-08-26 14:05:55
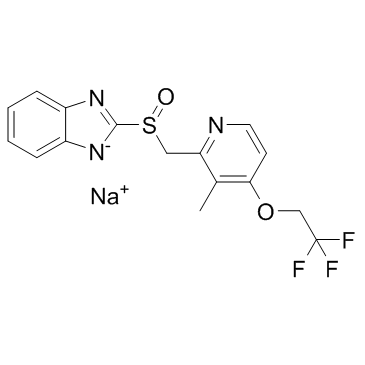
Lansoprazole (sodium) structure
|
Common Name | Lansoprazole (sodium) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 226904-00-3 | Molecular Weight | 391.34300 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H13F3N3NaO2S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Lansoprazole (sodium)Lansoprazole sodium(AG-1749) is a proton pump inhibitor which prevents the stomach from producing acid.Target: Proton PumpLansoprazole (sodium) is sodium salt form of lansoprazole, lansoprazole, a substituted benzimidizole proton pump inhibitor, on pharmacokinetics and metabolism of theophylline has been studied in healthy adults given oral lansoprazole 30 mg once daily for 11 days. On Days 4 and 11 of 300 mg aminophylline was simultaneously administered orally and blood samples for theophylline analysis were taken over 24 h [1]. Patients in the lansoprazole group were significantly less likely to have a recurrence of ulcer complications than patients in the placebo group (P=0.008). There was no significant difference in mortality between the two groups [2]. lansoprazole (AG-1749) and omeprazole, were found to have significant activities against this organism. The activity of lansoprazole was comparable to that of bismuth citrate, with MICs ranging from 3.13 to 12.5 micrograms/ml, and fourfold more potent than that of omeprazole [3]. Clinical indications: Duodenal ulcer; Esophagitis; Gastroesophageal reflux; Gastrointestinal disease; Helicobacter pylori infection; Peptic ulcer; Stomach ulcer; Ulcer; Zollinger-Ellison syndromeFDA Approved Date: May 10, 1995Toxicity: Symptoms of overdose include abdominal pain, nausea and diarrhea. |
| Name | sodium,2-[[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl]methylsulfinyl]benzimidazol-1-ide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Lansoprazole sodium(AG-1749) is a proton pump inhibitor which prevents the stomach from producing acid.Target: Proton PumpLansoprazole (sodium) is sodium salt form of lansoprazole, lansoprazole, a substituted benzimidizole proton pump inhibitor, on pharmacokinetics and metabolism of theophylline has been studied in healthy adults given oral lansoprazole 30 mg once daily for 11 days. On Days 4 and 11 of 300 mg aminophylline was simultaneously administered orally and blood samples for theophylline analysis were taken over 24 h [1]. Patients in the lansoprazole group were significantly less likely to have a recurrence of ulcer complications than patients in the placebo group (P=0.008). There was no significant difference in mortality between the two groups [2]. lansoprazole (AG-1749) and omeprazole, were found to have significant activities against this organism. The activity of lansoprazole was comparable to that of bismuth citrate, with MICs ranging from 3.13 to 12.5 micrograms/ml, and fourfold more potent than that of omeprazole [3]. Clinical indications: Duodenal ulcer; Esophagitis; Gastroesophageal reflux; Gastrointestinal disease; Helicobacter pylori infection; Peptic ulcer; Stomach ulcer; Ulcer; Zollinger-Ellison syndromeFDA Approved Date: May 10, 1995Toxicity: Symptoms of overdose include abdominal pain, nausea and diarrhea. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C16H13F3N3NaO2S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 391.34300 |
| Exact Mass | 391.05800 |
| PSA | 84.18000 |
| LogP | 4.01000 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| UNII-GV9NY1U369 |
| Lansoprazole sodium |
| Lansoprazole (sodium) |