I-138
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 16:32:27
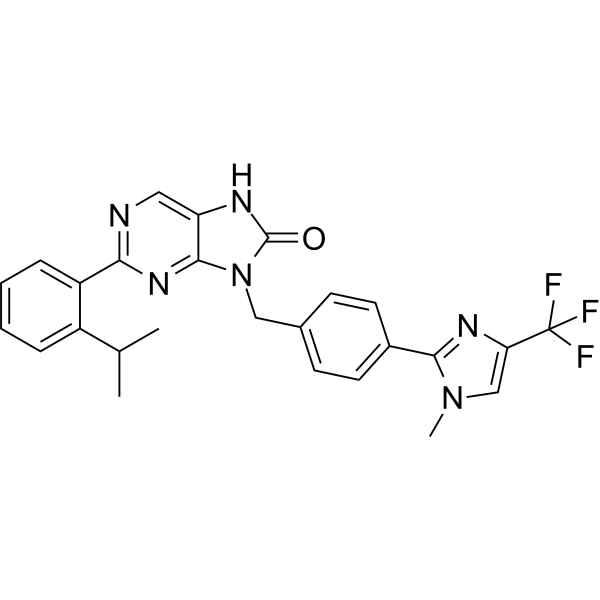
I-138 structure
|
Common Name | I-138 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2098211-50-6 | Molecular Weight | 492.50 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H23F3N6O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of I-138I-138 is an orally active compound structurally related to ML323 (HY-17543). I-138 and ML-323 are potent reversible inhibitors of USP1-UAF1. I-138 displays synergistic binding with ubiquitin and mutual exclusive binding with ML323. I-138 induces the monoubiquitination of FANCD2 and PCNA in MDA-MB-436 cells, increases PCNA and FANCD2 monoubiquitination in HAP-1 USP1 WT cells. I-138 ablates USP1 autocleavage in cells[1]. |
| Name | I-138 |
|---|
| Description | I-138 is an orally active compound structurally related to ML323 (HY-17543). I-138 and ML-323 are potent reversible inhibitors of USP1-UAF1. I-138 displays synergistic binding with ubiquitin and mutual exclusive binding with ML323. I-138 induces the monoubiquitination of FANCD2 and PCNA in MDA-MB-436 cells, increases PCNA and FANCD2 monoubiquitination in HAP-1 USP1 WT cells. I-138 ablates USP1 autocleavage in cells[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C26H23F3N6O |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 492.50 |