9-(2’-O-Acetyl-5’-O-benzoyl-3’-O-methyl-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-2,6-dichloropurine
Modify Date: 2025-12-01 12:30:47
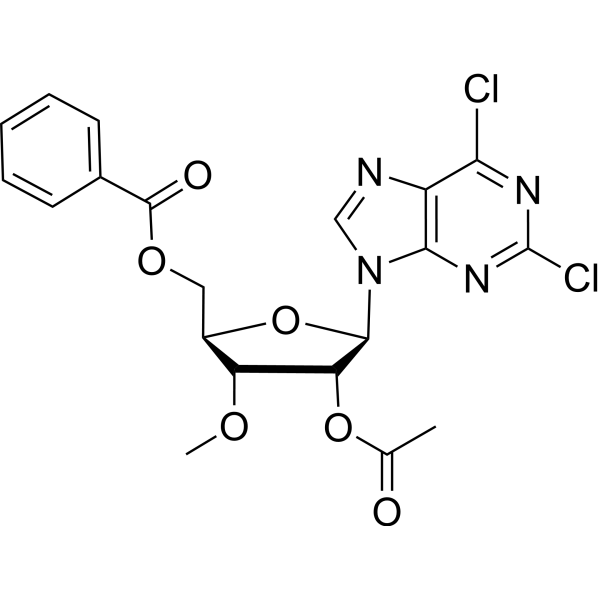
9-(2’-O-Acetyl-5’-O-benzoyl-3’-O-methyl-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-2,6-dichloropurine structure
|
Common Name | 9-(2’-O-Acetyl-5’-O-benzoyl-3’-O-methyl-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-2,6-dichloropurine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2072145-40-3 | Molecular Weight | 481.29 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H18Cl2N4O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of 9-(2’-O-Acetyl-5’-O-benzoyl-3’-O-methyl-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-2,6-dichloropurine9-(2’-O-Acetyl-5’-O-benzoyl-3’-O-methyl-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-2,6-dichloropurine is a purine nucleoside analog. Purine nucleoside analogs have broad antitumor activity targeting indolent lymphoid malignancies. Anticancer mechanisms in this process rely on inhibition of DNA synthesis, induction of apoptosis, etc[1]. |
| Name | 9-(2’-O-Acetyl-5’-O-benzoyl-3’-O-methyl-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-2,6-dichloropurine |
|---|
| Description | 9-(2’-O-Acetyl-5’-O-benzoyl-3’-O-methyl-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-2,6-dichloropurine is a purine nucleoside analog. Purine nucleoside analogs have broad antitumor activity targeting indolent lymphoid malignancies. Anticancer mechanisms in this process rely on inhibition of DNA synthesis, induction of apoptosis, etc[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C20H18Cl2N4O6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 481.29 |
| InChIKey | OZFIAZBMUUBMTO-SCFUHWHPSA-N |
| SMILES | COC1C(COC(=O)c2ccccc2)OC(n2cnc3c(Cl)nc(Cl)nc32)C1OC(C)=O |