Silver oxide
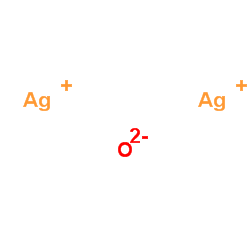
Silver oxide structure
|
Common Name | Silver oxide | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 20667-12-3 | Molecular Weight | 231.736 | |
| Density | 7,143 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | Ag2O | Melting Point | 300°C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |



GHS03, GHS05, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | silver,hydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 7,143 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 300°C (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | Ag2O |
| Molecular Weight | 231.736 |
| Exact Mass | 229.805099 |
| PSA | 9.23000 |
| InChIKey | NDVLTYZPCACLMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | [Ag+].[Ag+].[O-2] |
| Stability | Stable. Oxidiser. Incompatible with most common metals, ammonia, magnesium, many organic materials. |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS03, GHS05, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H271-H318-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P220-P273-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | O: Oxidizing agent;C: Corrosive; |
| Risk Phrases | R34;R8 |
| Safety Phrases | S17-S26-S36-S45-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN 1479 5.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | VW4900000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 5.1 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Structural studies of lead lithium borate glasses doped with silver oxide.
Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 86 , 392-8, (2012) Silver oxide doped lead lithium borate (LLB) glasses have been prepared and characterized. Structural and composition characterization were accessed by XRD, FTIR, Raman, SEM and EDS. Results from FTIR... |
|
|
Capture and activation of aerial CO2 by carbamoylation of L-threonine in a Ag(I) supramolecular framework.
Dalton Trans. 40(21) , 5677-9, (2011) An ultrasonic reaction of Ag(2)O, 4,4'-bipyridine (bipy) and (2S, 3R)-3-amino-2-hydroxybutanoic acid (L-Thr) gives an unexpected Ag(I) supramolecular framework, {[Ag(3)(bipy)(3)(cahba)]·HCO(3)·10H(2)O... |
|
|
Toxicity of silver nanoparticles at the air-liquid interface.
Biomed Res. Int. 2013 , 328934, (2013) Silver nanoparticles are one of the most prevalent nanomaterials in consumer products. Some of these products are likely to be aerosolized, making silver nanoparticles a high priority for inhalation t... |
| (argentiooxy)silver |
| silver(l) oxide |
| Disilver oxide |
| Silver(1+) oxide |
| Silver(I) oxide |
| silver hemioxide |
| Silver oxide |
| silver oxide (I) |
| Silver oxide (Ag2O) |
| Silver (I) Oxide |
| EINECS 243-957-1 |
| MFCD00003404 |
| Argentous oxide |
 CAS#:563-63-3
CAS#:563-63-3 CAS#:7440-22-4
CAS#:7440-22-4 CAS#:24703-63-7
CAS#:24703-63-7 CAS#:80937-33-3
CAS#:80937-33-3 Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/380/58034-59-6.png) CAS#:58034-59-6
CAS#:58034-59-6 CAS#:7732-18-5
CAS#:7732-18-5 CAS#:14641-64-6
CAS#:14641-64-6 CAS#:14866-68-3
CAS#:14866-68-3 CAS#:14325-99-6
CAS#:14325-99-6 CAS#:3794-64-7
CAS#:3794-64-7 CAS#:372-64-5
CAS#:372-64-5 CAS#:358-15-6
CAS#:358-15-6 CAS#:7783-61-1
CAS#:7783-61-1 CAS#:994-49-0
CAS#:994-49-0 CAS#:7783-99-5
CAS#:7783-99-5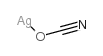 CAS#:3315-16-0
CAS#:3315-16-0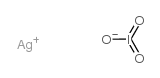 CAS#:7783-97-3
CAS#:7783-97-3
